Summary of research on flame 3D reconstruction based on computed tomography of chemiluminescence technology
-
摘要: 燃烧过程具有三维、高温、湍流、非稳态等特性,其精确测量存在一定的难度,一直是国内外研究的热点。化学发光计算断层成像(CTC)技术将化学发光技术和计算机断层成像(CT)技术相结合,通过直接拍摄不同角度的火焰图像,利用重构算法进行重建,可以快速准确地实现火焰三维结构的精细刻画。CTC系统以火焰的自发光作为光源,因此不需要额外的光源设备,这使得该系统具有容易搭建、可在复杂环境下实现等优势,可以用于高温、湍流火焰的实时测量,对于研究复杂燃烧流场、提高燃烧效率有着十分重要的意义。本文首先介绍了CTC技术的基本原理,然后从成像模型、重构算法、实验方法和应用方向4个方面介绍了CTC技术在火焰重构方向的研究进展,最后讨论了CTC技术的发展趋势。Abstract: Due to the characteristics of combustion such as three-dimension, high temperature, turbulence, and unsteady state accurate measurement of the combustion is difficult and is a hot research topic. Computed Tomography of Chemiluminescence (CTC) combines the chemiluminescence and CT technology. By directly shooting flame images from different angles and using reconstruction algorithms to reconstruct the flame, a fine description of the three-dimensional structure of the flame can be achieved quickly and accurately. The self-luminescence of the flame is used in the CTC as the light source, so there is no additional light source equipment required, which makes the system easy to build and can be implemented in a complex environment. These advantages enable the CTC technology to be used for real-time measurement of high temperature and turbulent flames, which is of great significance for studying complex combustion flow fields and improving combustion efficiency. In this paper, the basic principles of the CTC technology are introduced firstly, and then the research progress of the CTC technology in the direction of 3D reconstruction of flame is introduced in four aspects: the imaging model, the reconstruction algorithm, the experimental equipment and its application. Finally, the development trend of the CTC technology is discussed.
-
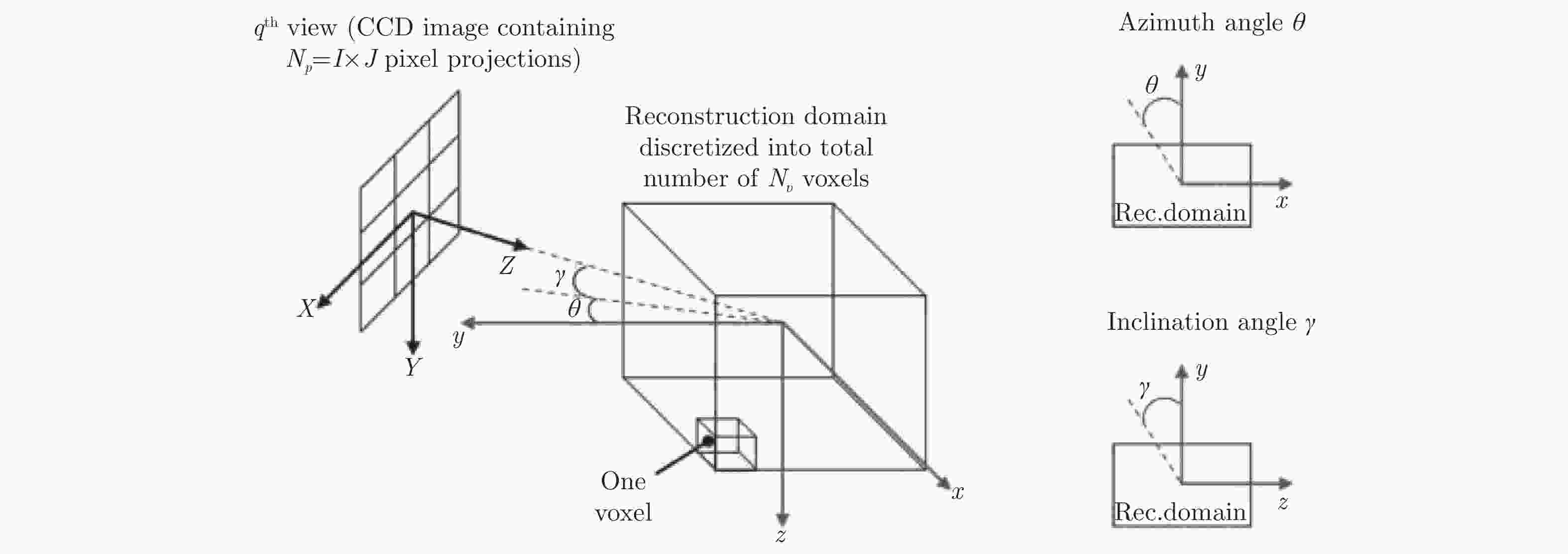
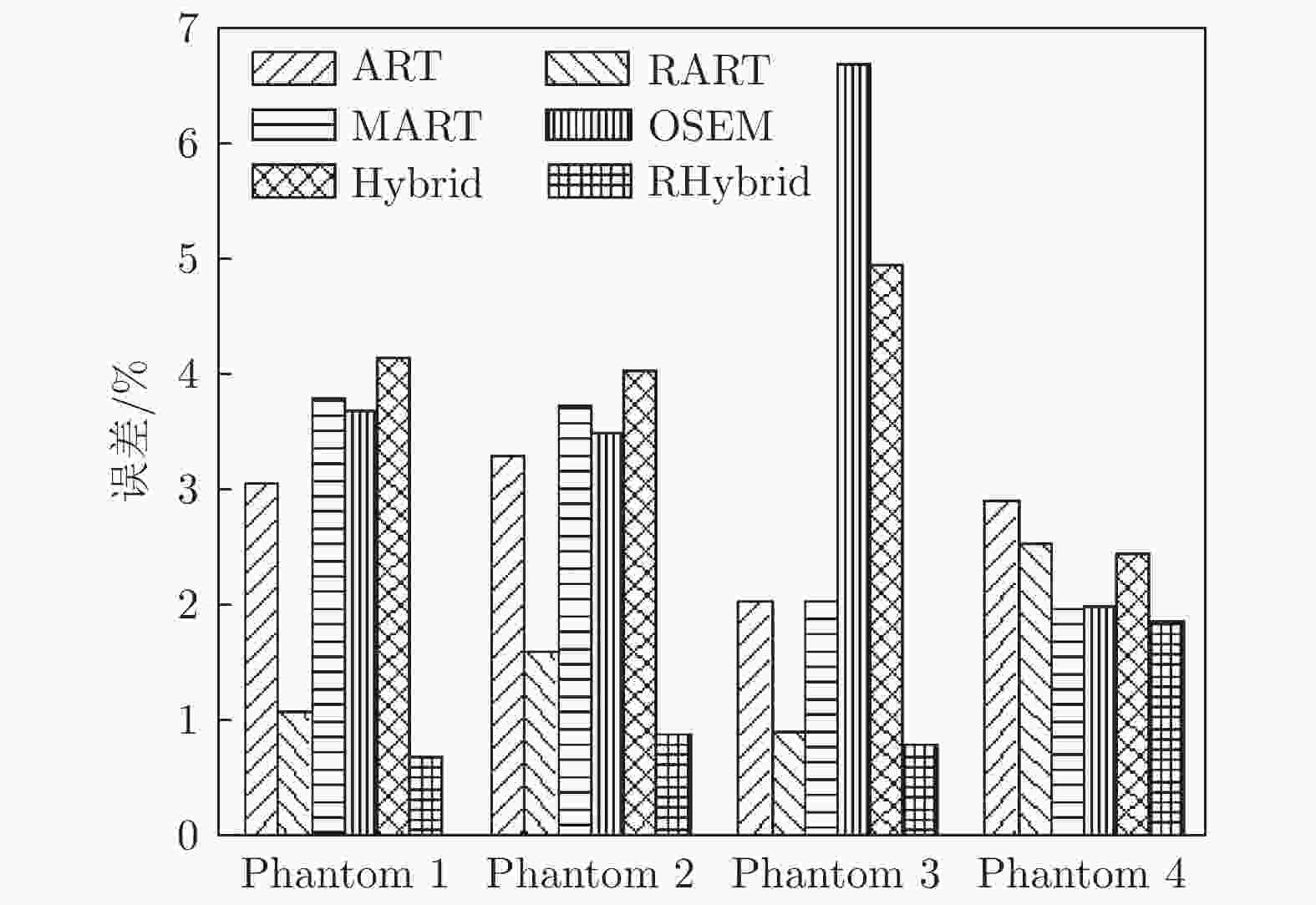
表 1 CTC重构算法的发展
Table 1. Development of CTC reconstruction algorithms
参考文献 成像模型 重建维度 改进方式及成果 [47] 线性成像模型 二维切片叠加 改进权系数矩阵计算方法,加快了重建速度 [49] 线性成像模型 二维切片叠加 将问题转化为二值问题,减少了投影角数量 [50] 线性成像模型 二维切片叠加 提出了使用退火模拟算法求解二元函数,提高了解决二元问题的效率 [24] 线性成像模型 三维重建 首次提出直接三维重建方式,提高了重建精度 [51] 线性成像模型 三维重建 提出了基于熵最大化并结合MENT的直接三维重建算法,减少了重建误差及计算时间 [52] 线性成像模型 三维重建 基于Mojette变换理论,研究了在小角度情况下的重建 [53-54] 线性成像模型 三维重建 提出了FBP算法分别与ART算法和SART算法结合的LFBP−ART和
LFBP−SART算法,提高了重建精度[30] 线性成像模型 三维重建 提出基于光线追踪的成像模型,减少了投影数量 [36] 点扩散函数成像模型 三维重建 提出使用点扩散函数成像模型,引入正则化条件,提高了重建精度 [57] 点扩散函数成像模型 三维重建 提出了点扩散函数的简化模型 [59-60] 点扩散函数成像模型 三维重建 结合相机的缺陷改进了成像模型 [61] 点扩散函数成像模型 三维重建 考虑了火焰自吸收问题,改善了成像过程中信号衰减的问题 表 2 不同实验方法的优缺点
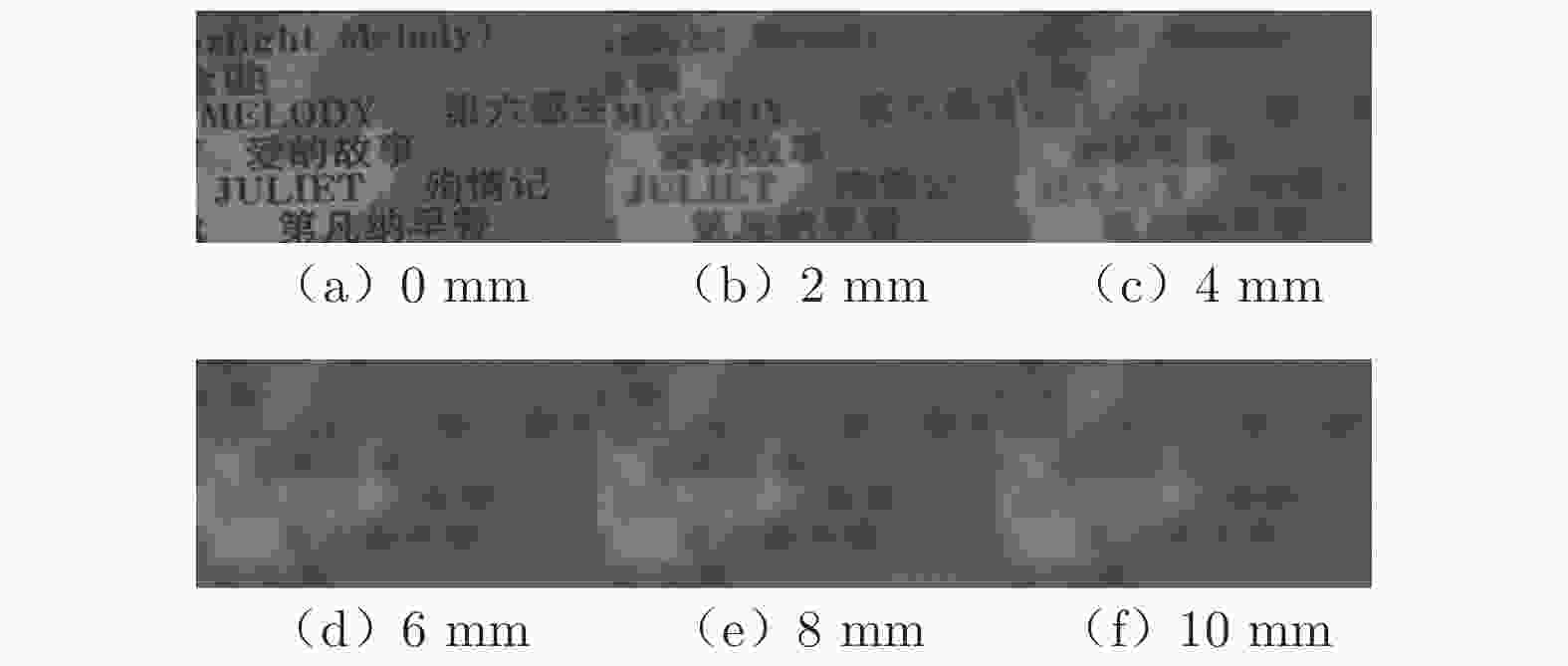
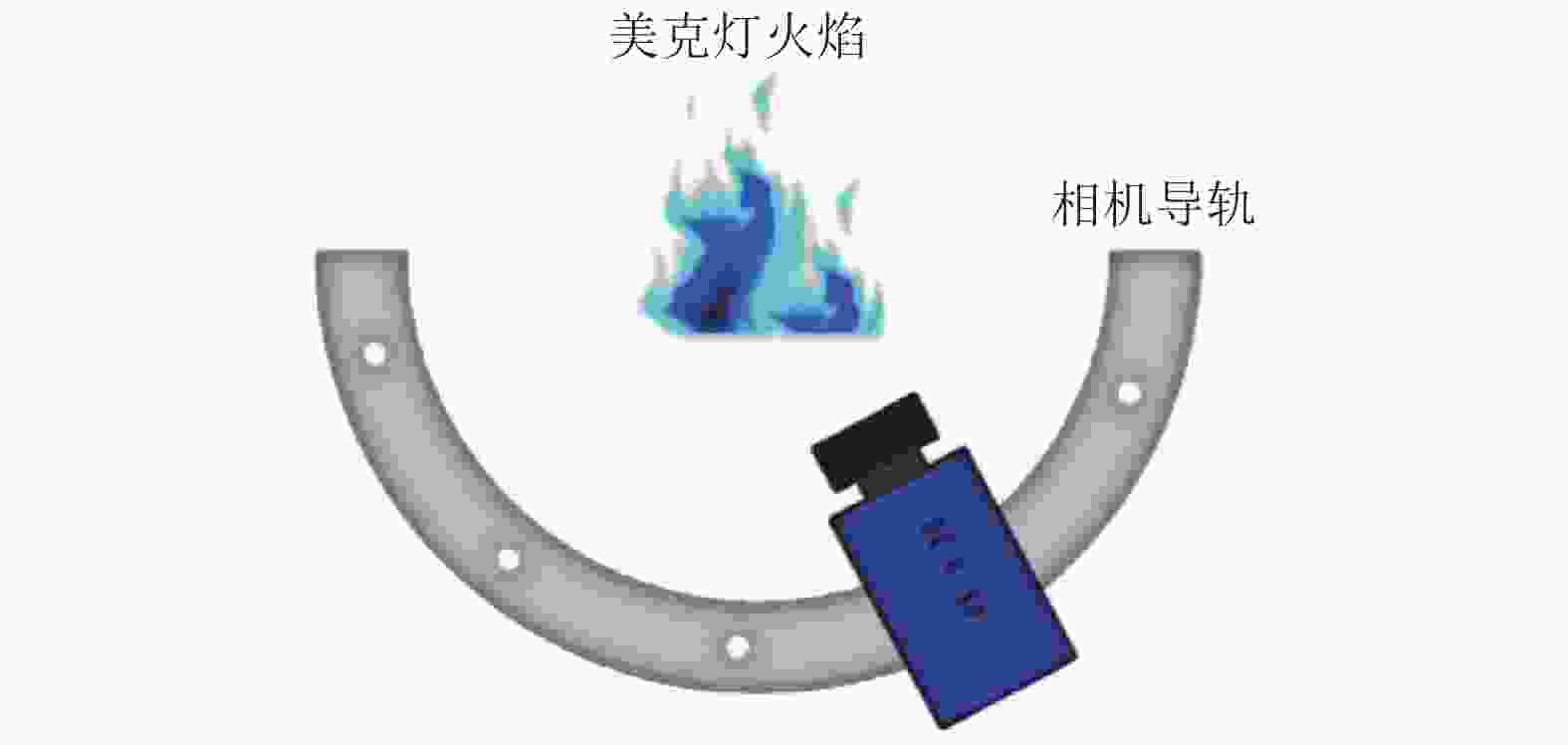
Table 2. Advantages and disadvantages of different experimental methods
实验方法 优点 缺点 直接相机拍摄法 实验布置简单;实验设备相对容易获得 多台相机的成本高;能获得的拍摄角度较少 相机 + 反射镜法 减少了相机的使用数量,降低了硬件成本 减少的数量有限,只能降低一半的相机数量;反射镜会降低拍摄精度且反射镜角度不容易精确获得 相机 + 光线内窥镜法 进一步减少相机的使用数量,降低成本;光纤内窥镜体积较小,相同空间内可以布置更多的投影角度 光纤束会造成光信号的损失;拍摄得到的图像信噪比相对较差 -
[1] 牛文, 李文杰. 美国空军圆满完成X-51A第四次试飞[J]. 飞航导弹, 2013(5): 3–4. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.2013.05.004NIU W, LI W J. The US Air Force successfully completed the fourth test flight of the X-51A[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2013(5): 3–4. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.2013.05.004 [2] YAN Y, QIU T, LU G. Recent advances in flame tomography[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2012, 20(2): 389–399. doi: 10.1016/S1004-9541(12)60402-9 [3] LIU S, CHEN Q, XIONG X, et al. Preliminary study on ECT imaging of flames in porous media[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2008, 19(9): 094017. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/19/9/094017 [4] ABDUL RAHIM R, CHAN K S, IBRAHIM S, et al. Fire-flame imaging using electrical capacitance tomography[J]. Jurnal Teknologi, 2006(45): 135–152. doi: 10.11113/jt.v45.335 [5] WATERFALL R C, HE R, WHITE N B, et al. Combustion imaging from electrical impedance measurements[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 1996, 7(3): 369–374. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/7/3/018 [6] HUANG S M, PLASKOWSKI A B, XIE C G, et al. Tomographic imaging of two-component flow using capacitance sensors[J]. Journal of Physics E: Scientific Instruments, 1989, 22(3): 173–177. doi: 10.1088/0022-3735/22/3/009 [7] YANG W Q, STOTT A L, BECK M S, et al. Development of capacitance tomographic imaging systems for oil pipeline measurements[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1995, 66(8): 4326–4332. doi: 10.1063/1.1145322 [8] MOHAMAD E J, RAHIM R A, IBRAHIM S, et al. Flame imaging using laser-based transmission tomography[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2006, 127(2): 332–339. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2005.12.031 [9] WONDRACZEK L, KHORSANDI A, WILLER U, et al. Mid-infrared laser-tomographic imaging of carbon monoxide in laminar flames by difference frequency generation[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2004, 138(1-2): 30–39. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2004.03.011 [10] WANG F, CEN K F, LI N, et al. Two-dimensional tomography for gas concentration and temperature distributions based on tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2010, 21(4): 045301. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/21/4/045301 [11] MA L. Single-shot 3D flame diagnostic based on volumetric laser induced fluorescence (VLIF)[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2017, 36(3): 4575–4583. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2016.07.050 [12] HUANG Q, WANG F, DONG L, et al. Reconstruction of soot temperature and volume fraction profiles of an asymmetric flame using stereoscopic tomography[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2009, 156(3): 565–573. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2009.01.001 [13] ZHOU B, WANG S M, XU C L, et al. 3D flame temperature reconstruction in optical sectioning tomography[C]//Proc of the 2009 IEEE International Workshop on Imaging Systems and Technique. 2009: 313-318. [14] HERTZ H M, FARIS G W. Emission tomography of flame radicals[J]. Optics Letters, 1988, 13(5): 351–353. doi: 10.1364/OL.13.000351 [15] SMART J, LU G, YAN Y, et al. Characterisation of an oxy-coal flame through digital imaging[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2010, 157(6): 1132–1139. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2009.10.017 [16] LU G, YAN Y, COLECHIN M. A digital imaging based multifunctional flame monitoring system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2004, 53(4): 1152–1158. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2004.830571 [17] YAN Y, LU G, COLECHIN M. Monitoring and characterisation of pulverised coal flames using digital imaging techniques[J]. Fuel, 2002, 81(5): 647–655. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(01)00161-2 [18] YIP B, LAM J K, WINTER M, et al. Time-resolved three-dimensional concentration measurements in a gas jet[J]. Science, 1987, 235(4793): 1209–1211. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4793.1209 [19] CHO K Y, SATIJA A, POURPOINT T L, et al. High-repetition-rate three-dimensional OH imaging using scanned planar laser-induced fluorescence system for multiphase combustion[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(3): 316–326. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.000316 [20] HARKER M R, HATTRELL T, LAWES M, et al. Measurements of the three-dimensional structure of flames at low turbulence[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2012, 184(10-11): 1818–1837. doi: 10.1080/00102202.2012.691775 [21] HULT J, OMRANE A, NYGREN J, et al. Quantitative three-dimensional imaging of soot volume fraction in turbulent non-premixed flames[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2002, 33(2): 265–269. doi: 10.1007/s00348-002-0410-2 [22] 宋尔壮, 雷庆春, 范玮. 基于层析原理的湍流火焰三维测量综述[J]. 实验流体力学, 2020, 34(1): 1–11. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20190135SONG E Z, LEI Q C, FAN W. A review on three-dimensional flame measurements based on tomography[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2020, 34(1): 1–11. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20190135 [23] FLOYD J. Computed Tomography of Chemiluminescence: A 3D Time Resolved Sensor for Turbulent Combustion[D]. London: Imperial College London, 2009. [24] KANG MW, LI X, MA L. Three-dimensional flame measurements using fiber-based endoscopes[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2015, 35(3): 3821–3828. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2014.07.064 [25] YU T, RUAN C, LIU H C, et al. Time-resolved measurements of a swirl flame at 4 kHz via computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(21): 5962–5969. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.005962 [26] MA L, LI X S, KANG M, et al. 3D flame measurements at 5 kHz on a jet fueled aviation combustor[C]//Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition. 2015. doi: 10.1115/GT2015-42823 [27] MA L. From ignition to stable combustion in a cavity flameholder studied via 3D tomographic chemiluminescence at 20 kHz[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2016, 165: 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2015.08.026 [28] 庄天戈. CT原理与算法[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 1992.ZHUANG T G. CT principle and algorithm[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 1992. [29] RADON J. On the determination of functions from their integral values along certain manifolds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1986, 5(4): 170–6. doi: 10.1109/TMI.1986.4307775 [30] CAI W W, LI X S, LI F, et al. Numerical and experimental validation of a three-dimensional combustion diagnostic based on tomographic chemiluminescence[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(6): 7050–7064. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.007050 [31] JIANG H. Computed Tomography Principles, Design, Artifacts, and Recent Advances[M]. 2nd Edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2009. [32] ANDERSEN A H, KAK A C. Simultaneous Algebraic Reconstruction Technique (SART): a superior implementation of the ART algorithm[J]. Ultrasonic Imaging, 1984, 6(1): 81–94. doi: 10.1016/0161-7346(84)90008-7 [33] JANSEN D P, HUTCHINS D A, UNGAR P J, et al. Acoustic tomography in solids using a bent ray sirt algorithm[J]. Nondestructive Testing and Evaluation, 1991, 6(3): 131–148. doi: 10.1080/10589759108953135 [34] ISHINO Y, OHIWA N. Three-Dimensional computerized tomographic reconstruction of instantaneous distribution of emission intensity in turbulent premixed flames[J]. Lean Combustion Technology II, 2001, 48(1): 25–29. [35] MOHRI K, GÖRS S, SCHÖLER J, et al. Instantaneous 3D imaging of highly turbulent flames using computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(26): 7385–7395. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.007385 [36] LI X, MA L. Capabilities and limitations of 3D flame measurements based on computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2015, 162(3): 642–651. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2014.08.020 [37] ZHOU B, WANG S M, XU C L, et al. 3-D flame temperature reconstruction in optical sectioning tomography[C]//Proc of the 2009 IEEE International Workshop on Imaging Systems and Techniques, Shenzhen. IEEE, 2009: 313-318. doi: 10.1109/IST.2009.5071656 [38] CAI W W, LI X S, WICKERSHAM A, et al. Three-dimensional combustion diagnostics based on computed tomography of chemiluminescence[C]//Proc of the 51st AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Grapevine. 2013: 557. doi: 10.2514/6.2013-557 [39] MA L, LEI Q C, WU Y, et al. 3D measurements of ignition processes at 20 kHz in a supersonic combustor[J]. Applied Physics B, 2015, 119(2): 313–318. doi: 10.1007/s00340-015-6066-4 [40] ITO T, ICHIKAWA R, KOISHI R, et al. Measurement of space variant PSF and its application to restoring severely degraded images[C]//Proc of the SICE Annual Conference. 2008: 142-145. [41] ITO T, FUJII Y, OHTA N, et al. Measurement of space variant PSF for restoring degraded images by security cameras[C]//Proc of the 2006 SICE-ICASE International Joint Conference. 2007: 2542-2545. [42] WANG J, SONG Y, LI Z H, et al. Multi-directional 3D flame chemiluminescence tomography based on lens imaging[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(7): 1231–1234. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.001231 [43] CAI W W, LI X S, MA L. Practical aspects of implementing three-dimensional tomography inversion for volumetric flame imaging[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(33): 8106–8116. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.008106 [44] YU T, CAI W W. Benchmark evaluation of inversion algorithms for tomographic absorption spectroscopy[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(8): 2183–2194. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.002183 [45] 张顺利, 张定华, 李山, 等. ART算法快速图像重建研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2006, 42(24): 1–3. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2006.24.001ZHANG S L, ZHANG D H, LI S, et al. Research of fast image reconstruction on ART algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2006, 42(24): 1–3. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2006.24.001 [46] 张顺利, 张定华, 赵歆波. 代数重建法中的一种快速投影系数计算方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2007, 24(5): 38–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2007.05.011ZHANG S L, ZHANG D H, ZHAO X B. Approach for fast projection coefficient computation in algebraic reconstruction technique[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2007, 24(5): 38–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2007.05.011 [47] 张顺利, 张定华, 王凯, 等. 一种基于ART算法的快速图像重建技术[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2007, 27(3): 479–483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2007.03.015ZHANG S L, ZHANG D H, WANG K, et al. A fast image reconstruction technique based on ART[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2007, 27(3): 479–483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2007.03.015 [48] CAI W W, MA L. Comparison of approaches based on optimization and algebraic iteration for binary tomography[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2010, 181(12): 1974–1981. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2010.09.004 [49] LI X, MA L. Minimizing binary functions with simulated annealing algorithm with applications to binary tomography[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2012, 183(2): 309–315. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2011.10.011 [50] GOYAL A, CHAUDHRY S, SUBBARAO P M V. Direct three dimensional tomography of flames using maximization of entropy technique[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2014, 161(1): 173–183. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2013.07.024 [51] WANG J, LI M Z, CHENG J X, et al. Exact reconstruction condition for angle-limited computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(15): 4273–4281. doi: 10.1364/AO.420223 [52] GILABERT G, LU G, YAN Y. Three-dimensional tomographic reconstruction of the luminosity distribution of a combustion flame[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2007, 56(4): 1300–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2007.900161 [53] HOSSAIN M M, LU G, YAN Y. Measurement of flame temperature distribution using optical tomographic and two-color pyrometric techniques[C]//Proc of the 2012 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings. 2012: 1856-1860. doi: 10.1109/I2MTC.2012.6229354 [54] LIU H C, YU T, ZHANG M, et al. Demonstration of 3D computed tomography of chemiluminescence with a restricted field of view[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(25): 7107–7115. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.007107 [55] WANG K, LI F, ZENG H, et al. Three-dimensional flame measurements with large field angle[J]. Optics express, 2017, 25(18): 21008–21018. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.021008 [56] MA L, CAI W W. Numerical investigation of hyperspectral tomography for simultaneous temperature and concentration imaging[J]. Applied Optics, 2008, 47(21): 3751–3759. doi: 10.1364/AO.47.003751 [57] CAI W W, MA L. Applications of critical temperature in minimizing functions of continuous variables with simulated annealing algorithm[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2010, 181(1): 11–16. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2009.08.001 [58] YU T, LIU H C, CAI W W. On the quantification of spatial resolution for three-dimensional computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(20): 24093–24108. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.024093 [59] YU T, LI Z M, RUAN C, et al. Development of an absorption-corrected method for 3D computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2019, 30(4): 045403. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ab01c1 [60] ISHINO Y, TAKEUCHI K, SHIGA S, et al. Non-scanning 3D-CT measurement with 40-lens tracking camera for turbulent propane/air rich-premixed flame[C]//Proc of the 6th International Energy Conversion Engineering Conference (IECEC). 2008: 5664. doi: 10.2514/6.2008-5664 [61] BHEEMUL H C, LU G, YAN Y. Three-dimensional visualization and quantitative characterization of gaseous flames[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2002, 13(10): 1643–1650. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/13/10/318 [62] 万明罡. 火焰化学发光三维重建方法的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2016.WAN M G. Research on three-dimensional flame reconstruction method based on chemiluminescence[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2016. [63] LIU Y, TAN J G, WAN M G, et al. OH* and CH* chemiluminescence characteristics in low swirl methane-air flames[J]. AIP Advances, 2020, 10(5): 055318. doi: 10.1063/5.0002660 [64] 徐萌. 基于CCD和光学层析成像算法的火焰三维温度场重建与实验研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2016.XU M. Reconstruction of 3D temperature field based on CCD and optical tomography algorithm[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2016. [65] LI X S, MA L. Volumetric imaging of turbulent reactive flows at kHz based on computed tomography[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(4): 4768–4778. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.004768 [66] MA L, WU Y, LEI Q, et al. 3D flame topography and curvature measurements at 5 kHz on a premixed turbulent Bunsen flame[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2016, 166: 66–75. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2015.12.031 [67] FLOYD J, KEMPF A M. Computed Tomography of Chemiluminescence (CTC): high resolution and instantaneous 3-D measurements of a Matrix burner[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2011, 33(1): 751–758. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2010.06.015 [68] FLOYD J, GEIPEL P, KEMPF A M. Computed Tomography of Chemiluminescence (CTC): instantaneous 3D measurements and Phantom studies of a turbulent opposed jet flame[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2011, 158(2): 376–391. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2010.09.006 [69] HOSSAIN M M, LU G, YAN Y. Optical fiber imaging based tomographic reconstruction of burner flames[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2012, 61(5): 1417–1425. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2012.2186477 [70] ANIKIN N B, SUNTZ R, BOCKHORN H. Tomographic reconstruction of the OH*-chemiluminescence distribution in premixed and diffusion flames[J]. Applied Physics, 2010, 100(3): 675–694. doi: 10.1007/s00340-010.4051-5 [71] ANIKIN N B, SUNTZ R, BOCKHORN H. Tomographic reconstruction of 2D-OH^-chemiluminescence distributions in turbulent diffusion flames[J]. Applied Physics B, 2012, 107(3): 591–602. doi: 10.1007/s00340-012-5003-z [72] HOSSAIN M M, LU G, YAN Y. Three-dimensional reconstruction of combustion flames through optical fiber sensing and CCD imaging[C]//Proc of the 2011 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference. 2011: 1-5. doi: 10.1109/IMTC.2011.5944306 [73] HOSSAIN M M, LU G, YAN Y. Three-dimensional reconstruction of flame temperature and emissivity through tomographic imaging and pyrometric measurement[C]//2012 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques Proceedings. IEEE, 2012: 13-17. [74] HOSSAIN M M, LU G, YAN Y. Three-dimensional reconstruction of flame temperature and emissivity through tomographic imaging and pyrometric measurement[C]//Proc of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques Proceedings. 2012: 13-17. doi: 10.1109/IST. 2012.6295577 [75] KANG MW. Investigation of Endoscopic Techniques for Flow and Combustion Measurements[D]. Virginia: Virginia Tech, 2014. [76] LIU H, ZHAO J, SHUI C, et al. Reconstruction and analysis of non-premixed turbulent swirl flames based on kHz-rate multi-angular endoscopic volumetric tomography[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 91: 422–433. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.05.025 [77] WANG K L, LI F, ZENG H, et al. Computed tomography measurement of 3D combustion chemiluminescence using single camera[C]//Proc SPIE 10155, Optical Measurement Technology and Instrumentation. 2016: 792-797. doi: 10.1117/12.2247303 [78] ZHOU G, LI F, WANG K, et al. Research on quantitative method for three-dimensional computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(17): 5310–5318. doi: 10.1364/AO.393225 [79] RUAN C, YU T, CHEN F, et al. Experimental characterization of the spatiotemporal dynamics of a turbulent flame in a gas turbine model combustor using computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Energy, 2019, 170(MAR.1): 744–751. [80] ZHAO J N, LIU H C, CAI W W. Numerical and experimental validation of a single-camera 3D velocimetry based on endoscopic tomography[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(6): 1363–1373. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.001363 [81] KANG M, WU Y, MA L. Fiber-based endoscopes for 3D combustion measurements: view registration and spatial resolution[J]. Combustion and flame, 2014, 161(12): 3063–3072. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2014.06.002 [82] BOLAN J, JOHNSON K C, THUROW B S. Preliminary Investigation of Three-Dimensional Flame Measurements with a Plenoptic Camera[C]// Proc of Aiaa Aerodynamic Measurement Technology & Ground Testing Conference. 2014. [83] HUANG Y, YAN Y. Transient two-dimensional temperature measurement of open flames by dual-spectral image analysis[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2000, 22(5): 371–384. doi: 10.1177/014233120002200503 [84] 周怀春, 娄新生, 尹鹤龄, 等. 单色火焰图象处理技术在锅炉燃烧监控中的应用研究[J]. 电力系统自动化, 1996, 20(10): 18–22.ZHOU H C, LOU X S, YIN H L, et al. Study on application of monochromatic flame image processing technique in combustion monitoring and control of boilers[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 1996, 20(10): 18–22. [85] YAN Z, LIANG Q, GUO Q, et al. Experimental investigations on temperature distributions of flame sections in a bench-scale opposed multi-burner gasifier[J]. Applied Energy, 2009, 86(7-8): 1359–1364. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2008.09.020 [86] LIU D, HUANG Q, WANG F, et al. Simultaneous Measurement of three-dimensional soot temperature and volume fraction fields in axisymmetric or Asymmetric small unconfined flames with CCD Cameras[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2010, 132(6): 1. doi: 10.1115/1.4000752 [87] TIMMERMAN B H, BRYANSTON-CROSS P J. Optical investigation of heat release and NOx production in combustion[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2007, 85: 012007. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/85/1/012007 [88] SAMARASINGHE J, PELUSO S, SZEDLMAYER M, et al. Three-dimensional chemiluminescence imaging of unforced and forced swirl-stabilized flames in a lean premixed multi-nozzle can combustor[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2013, 135(10): 101503. doi: 10.1115/1.4024987 [89] SAMARASINGHE J, PELUSO S J, QUAY B D, et al. The three-dimensional structure of swirl-stabilized flames in a lean premixed multinozzle can combustor[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2016, 138(3): 031502. doi: 10.1115/1.4031439 [90] DURAISAMY K, IACCARINO G, XIAO H. Turbulence modeling in the age of data[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 51: 357–377. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-010518-040547 [91] WANG Z Y, SONG C F, CHEN T. Deep learning based monitoring of furnace combustion state and measurement of heat release rate[J]. Energy, 2017, 131: 106–112. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.05.012 [92] PÁL T, ATTILA G, BERNADETT G. Image-based deep neural network prediction of the heat output of a step-grate biomass boiler[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 200: 155–169. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.05.080 [93] YU T, CAI W W, LIU Y Z. Rapid tomographic reconstruction based on machine learning for time-resolved combustion diagnostics[J]. The Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89(4): 043101. doi: 10.1063/1.5016403[PubMed [94] HUANG J, LIU H, WANG Q, et al. Limited-projection volumetric tomography for time-resolved turbulent combustion diagnostics via deep learning[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 106: 106123. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.106123 [95] FUKAMI K, FUKAGATA K, TAIRA K. Super-resolution reconstruction of turbulent flows with machine learning[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 870: 106–120. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2019.238 [96] FUKAMI K, FUKAGATA K, TAIRA K. Machine-learning-based spatio-temporal super resolution reconstruction of turbulent flows[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 909: A9. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2020.948 [97] PAN H J, ZHANG F H, LI X S, et al. Learning implicit light propagation from multi-flame projections for computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(22): 6469–6478. doi: 10.1364/AO.427578 [98] HUANG J Q, LIU H C, CAI W W. Online in situ prediction of 3D flame evolution from its history 2D projections via deep learning[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 875: R2. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2019.545 [99] YU T, LIU H C, ZHANG J Q, et al. Toward real-time volumetric tomography for combustion diagnostics via dimension reduction[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(5): 1107–1110. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.001107 [100] CHENG Y T, CHI F, WANG J J, et al. 3-D flame chemiluminescence tomography imaging under limited projection angle conditions: constraints and improving[C]//Proc of the 2019 International Conference on Optical Instruments and Technology: Optical Systems and Modern Optoelectronic Instruments. 2020. doi: 10.1117/12.2548769 -







 下载:
下载: