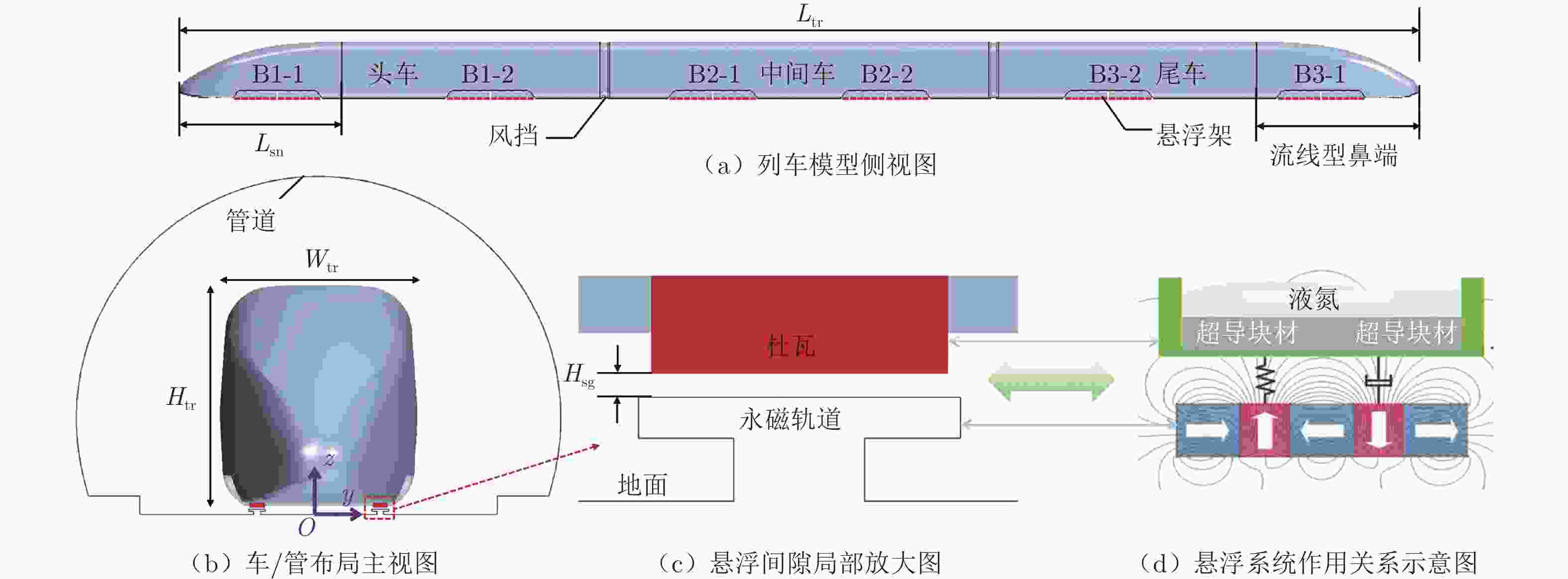
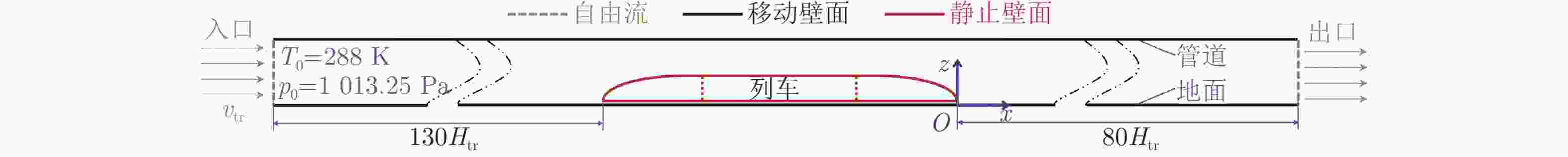
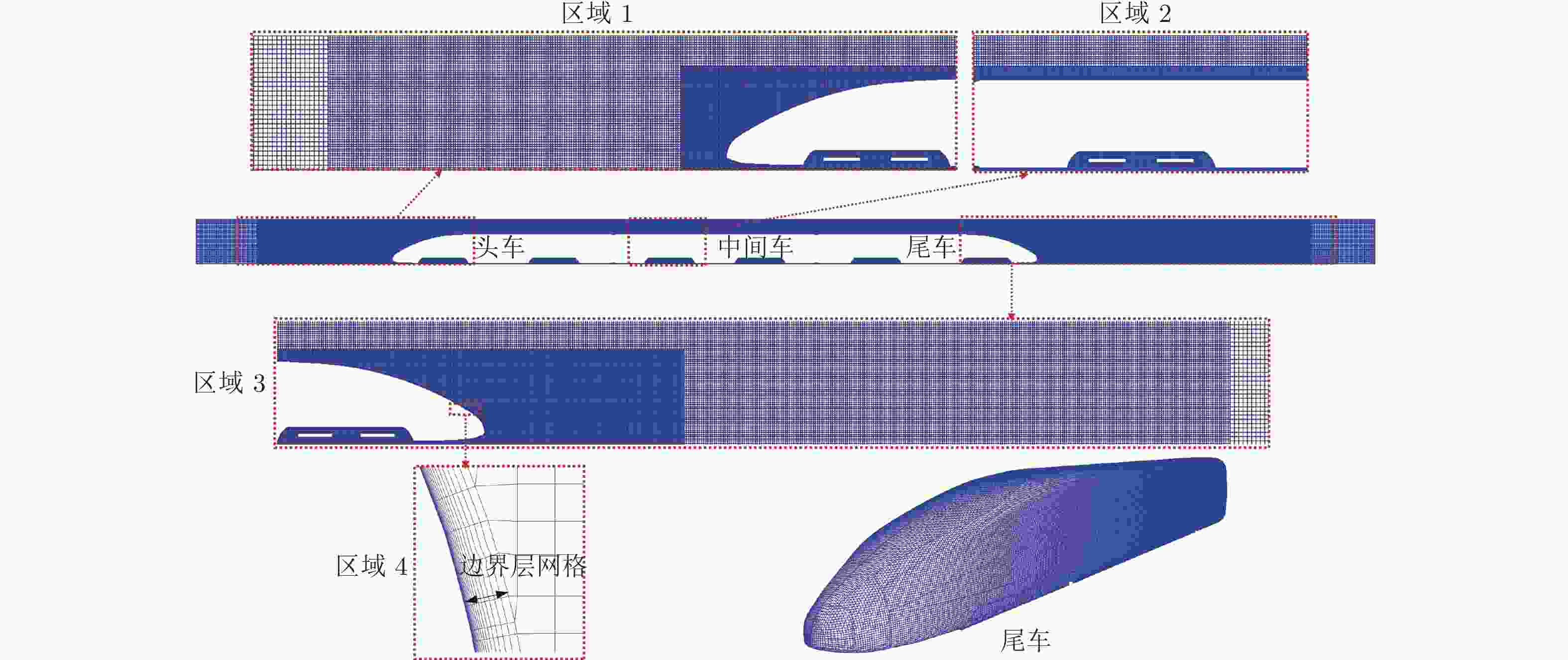
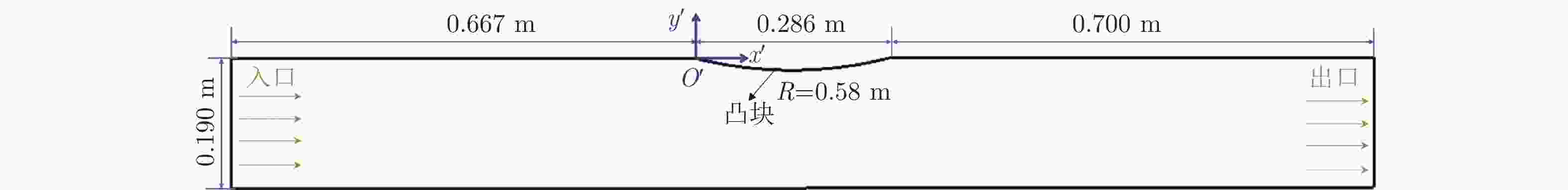
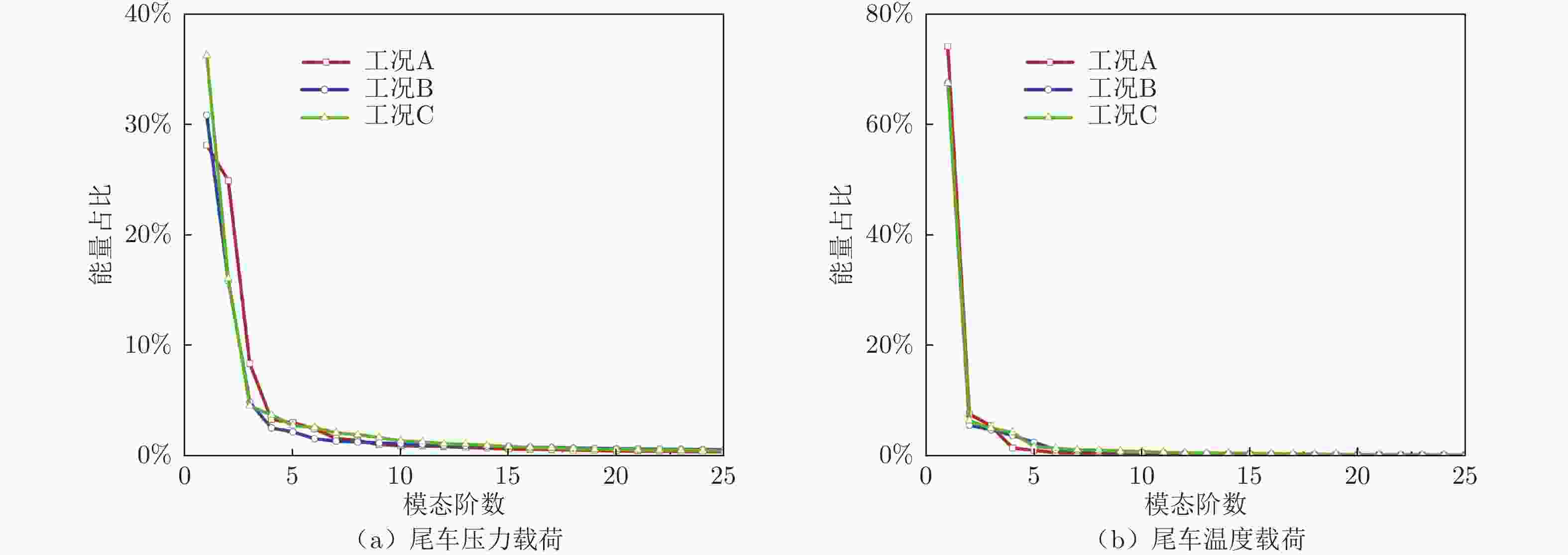
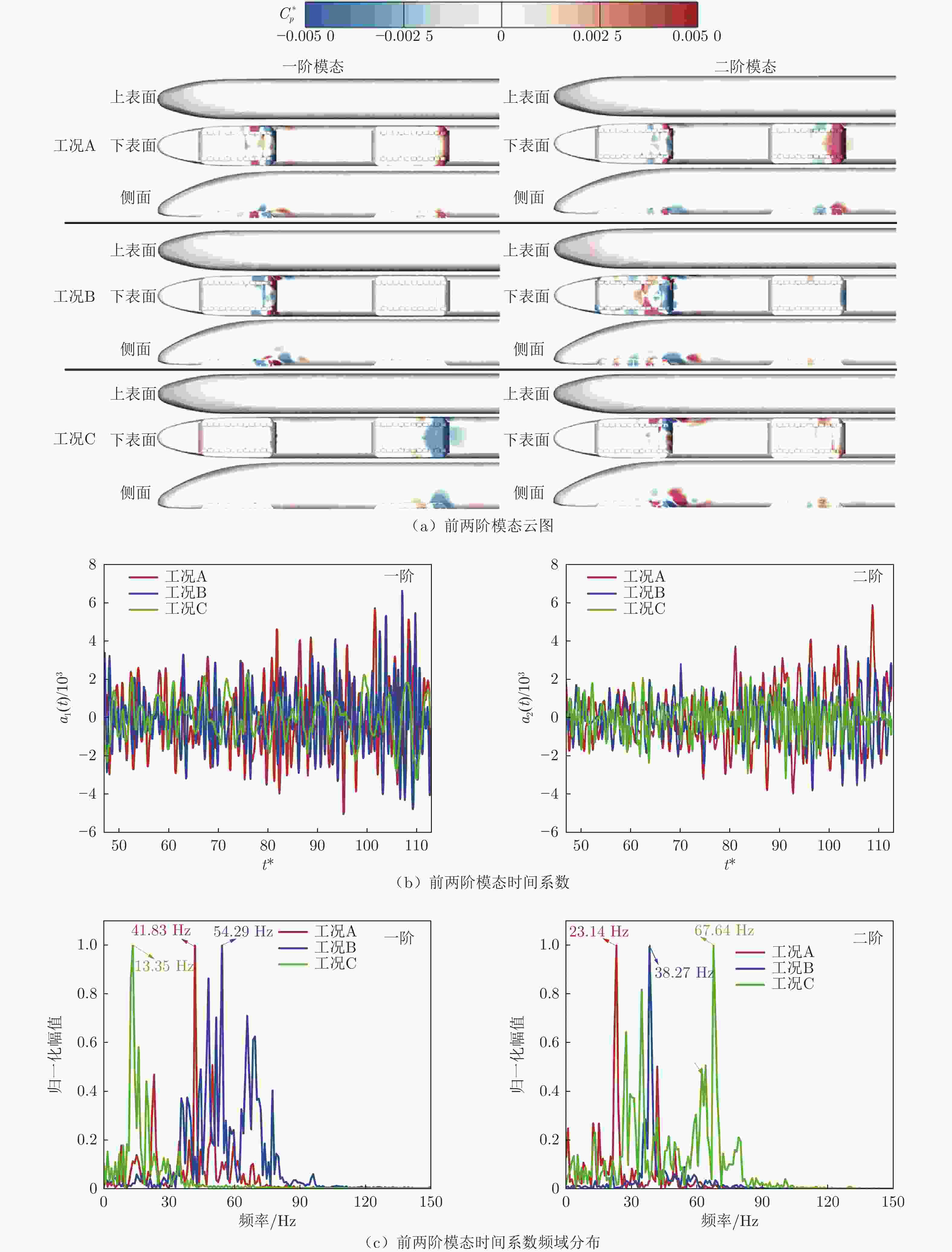
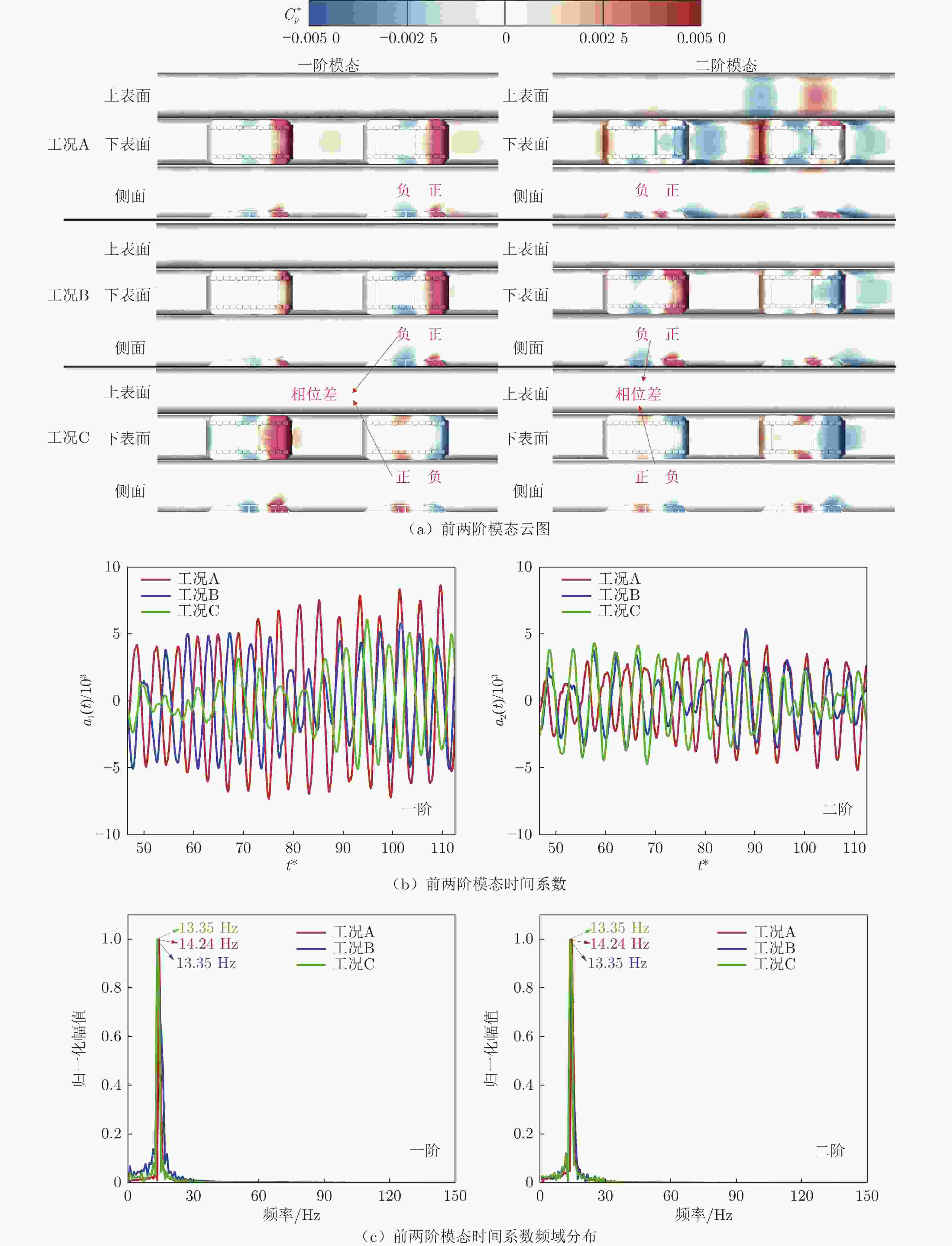
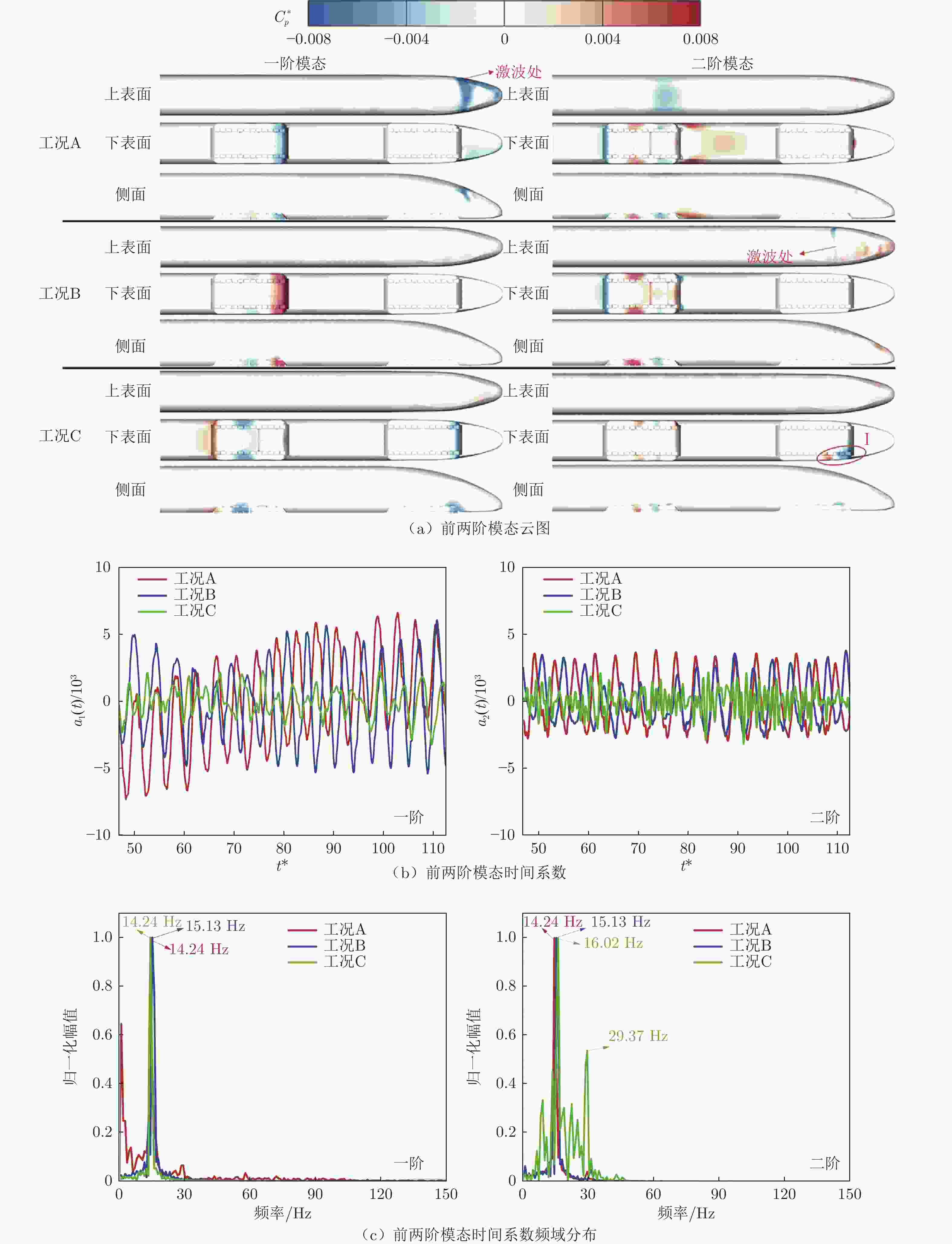
Distribution and unsteady characteristics of the temperature and pressure loads acting on the car-body in evacuated tube maglev transport
-
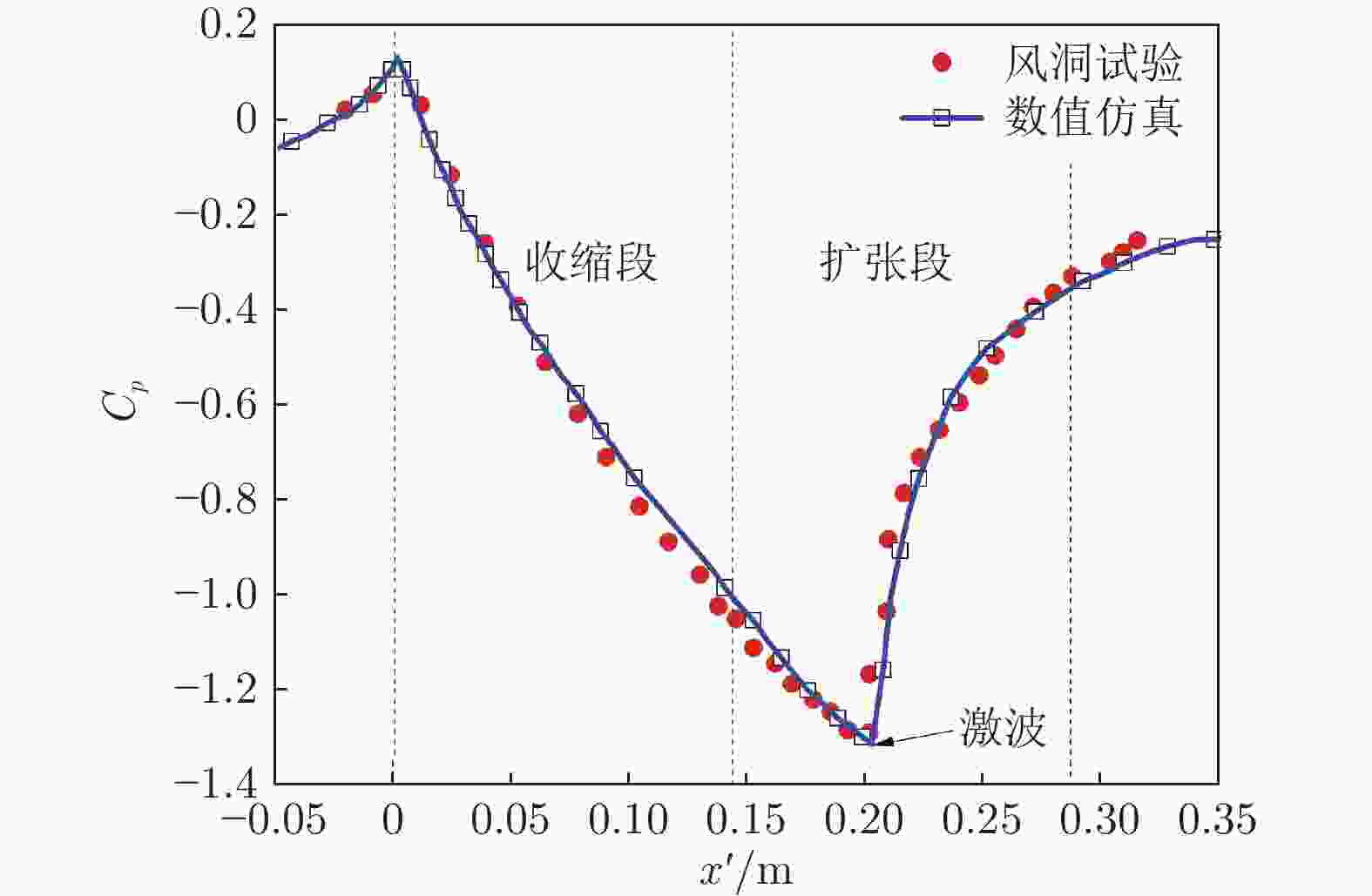
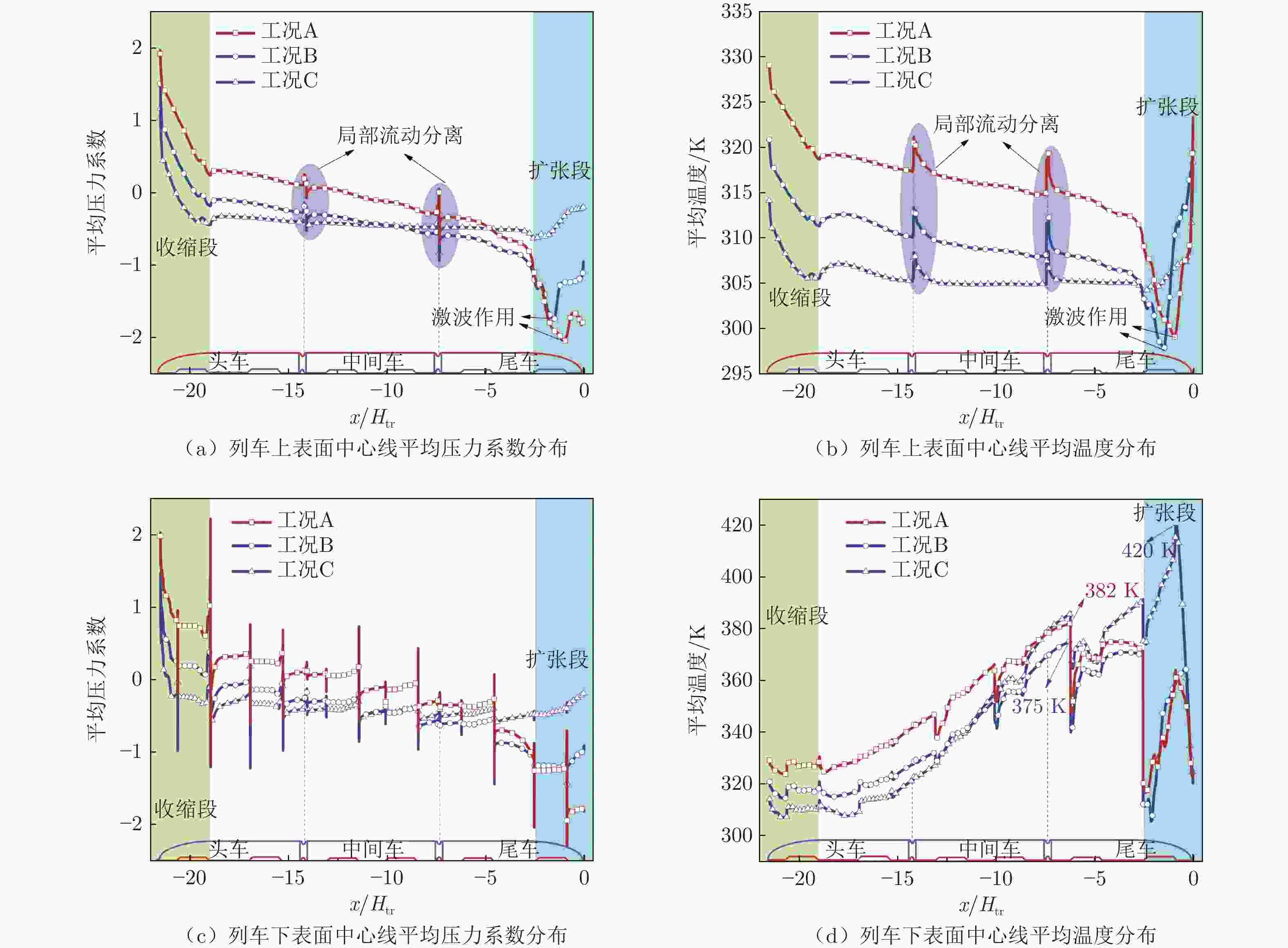
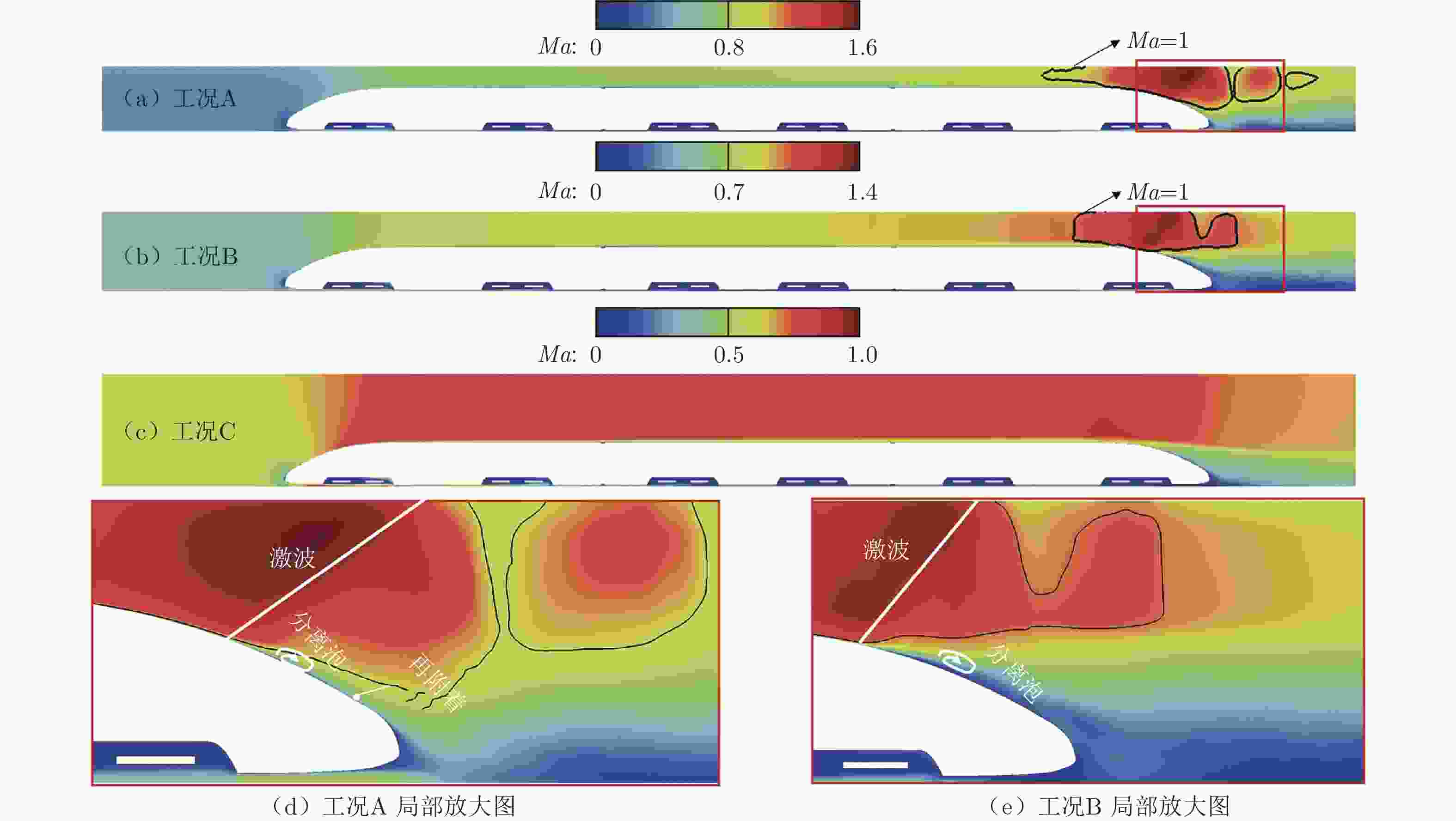
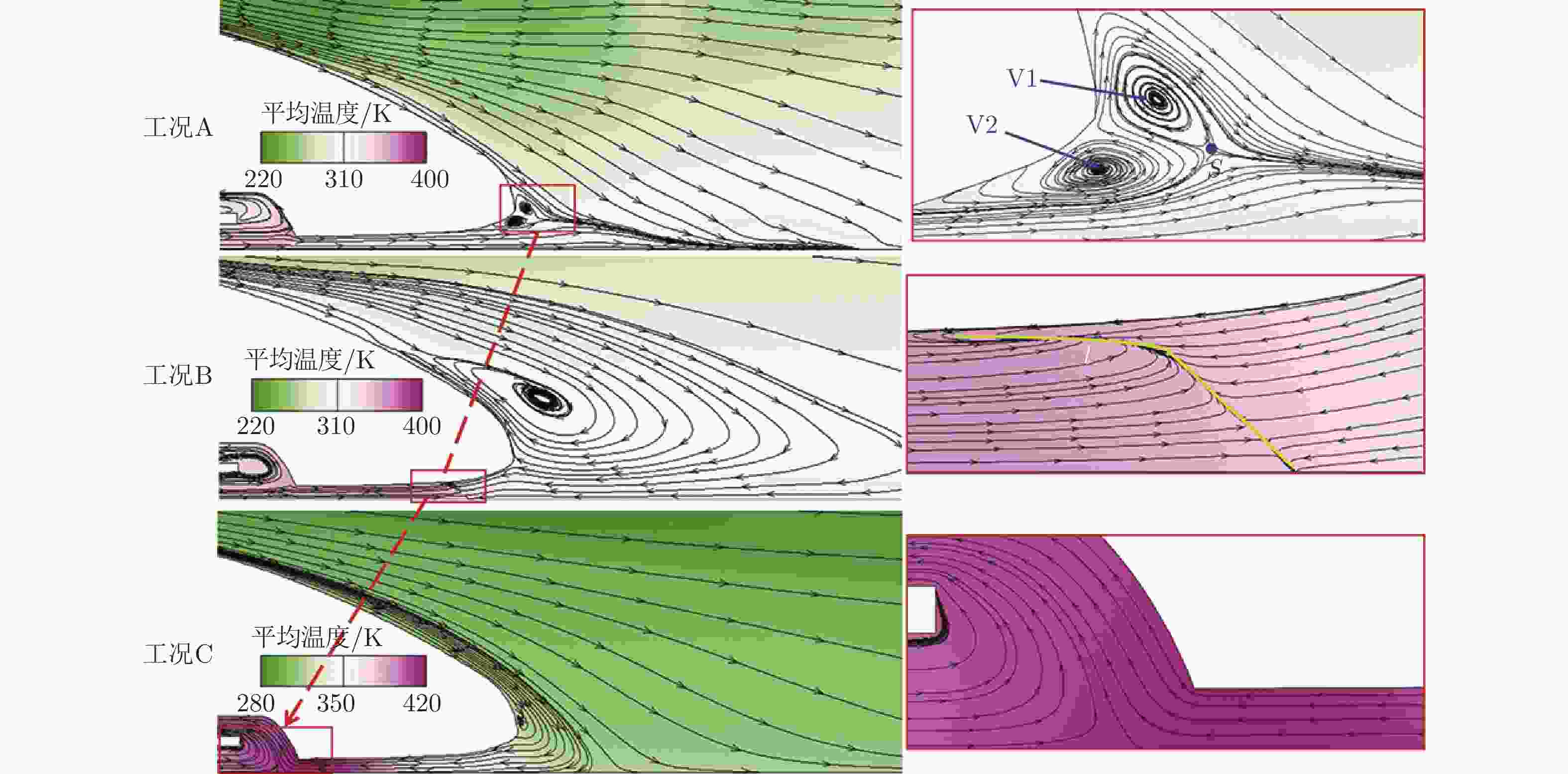
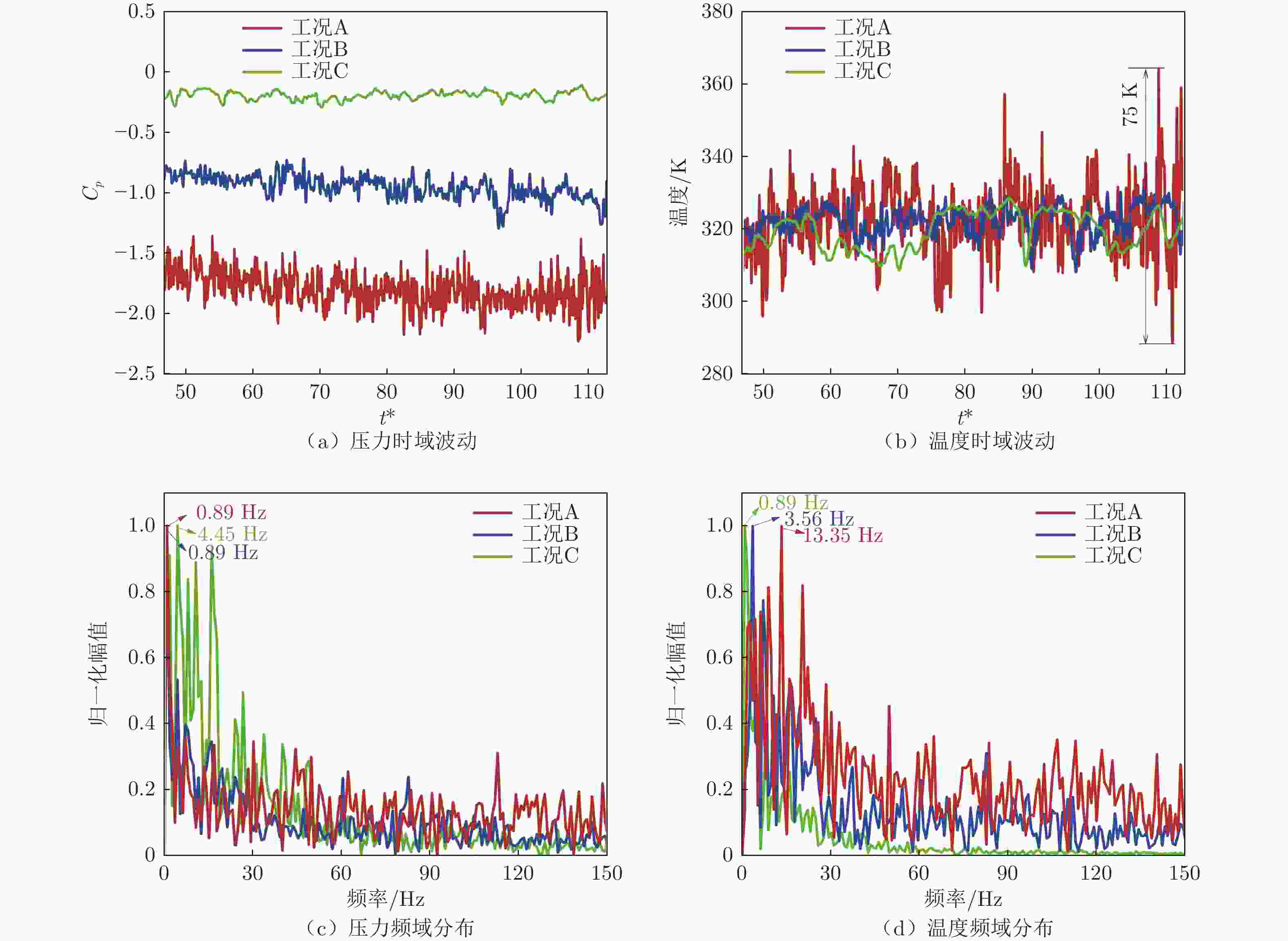
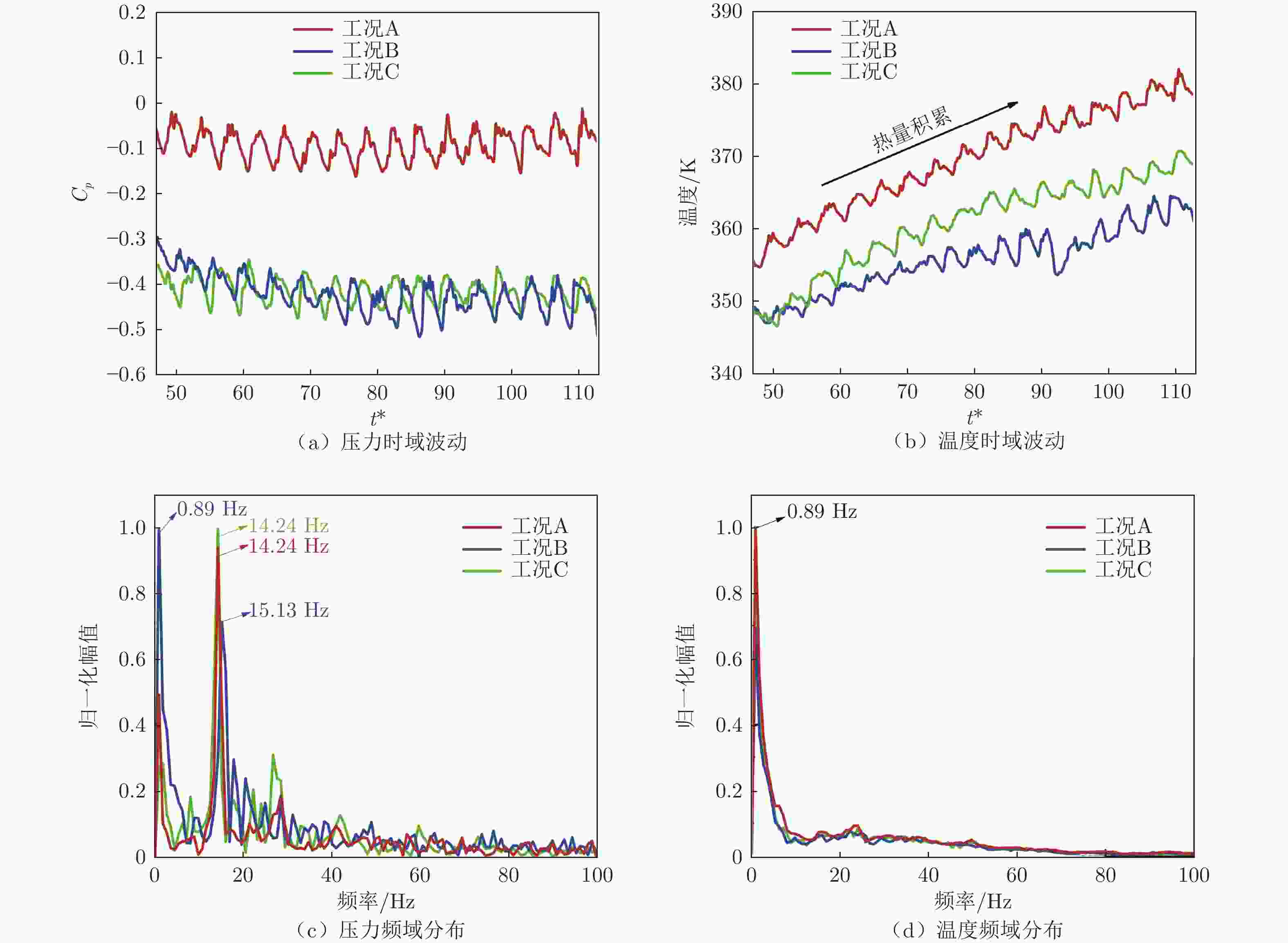
摘要: 基于SST
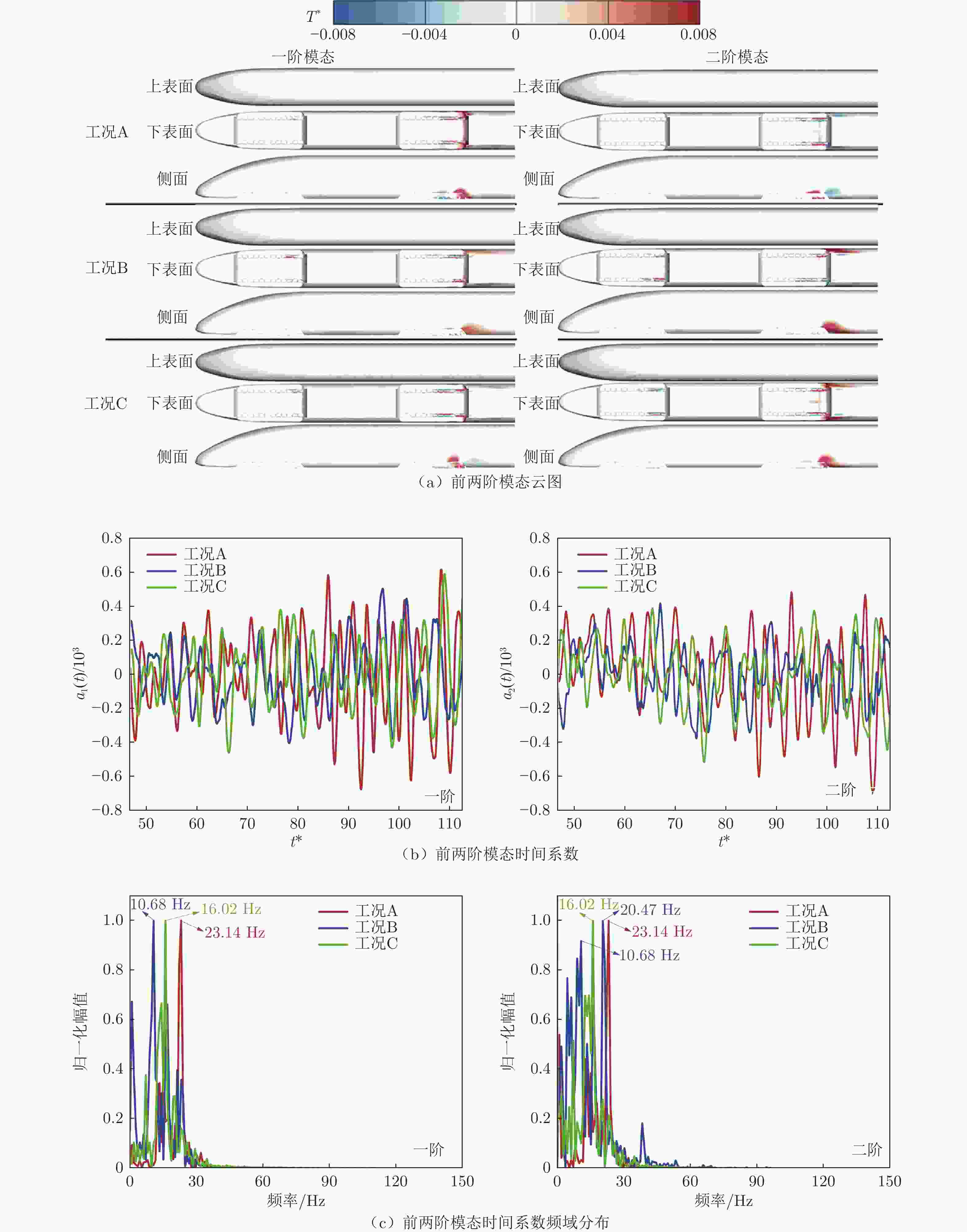
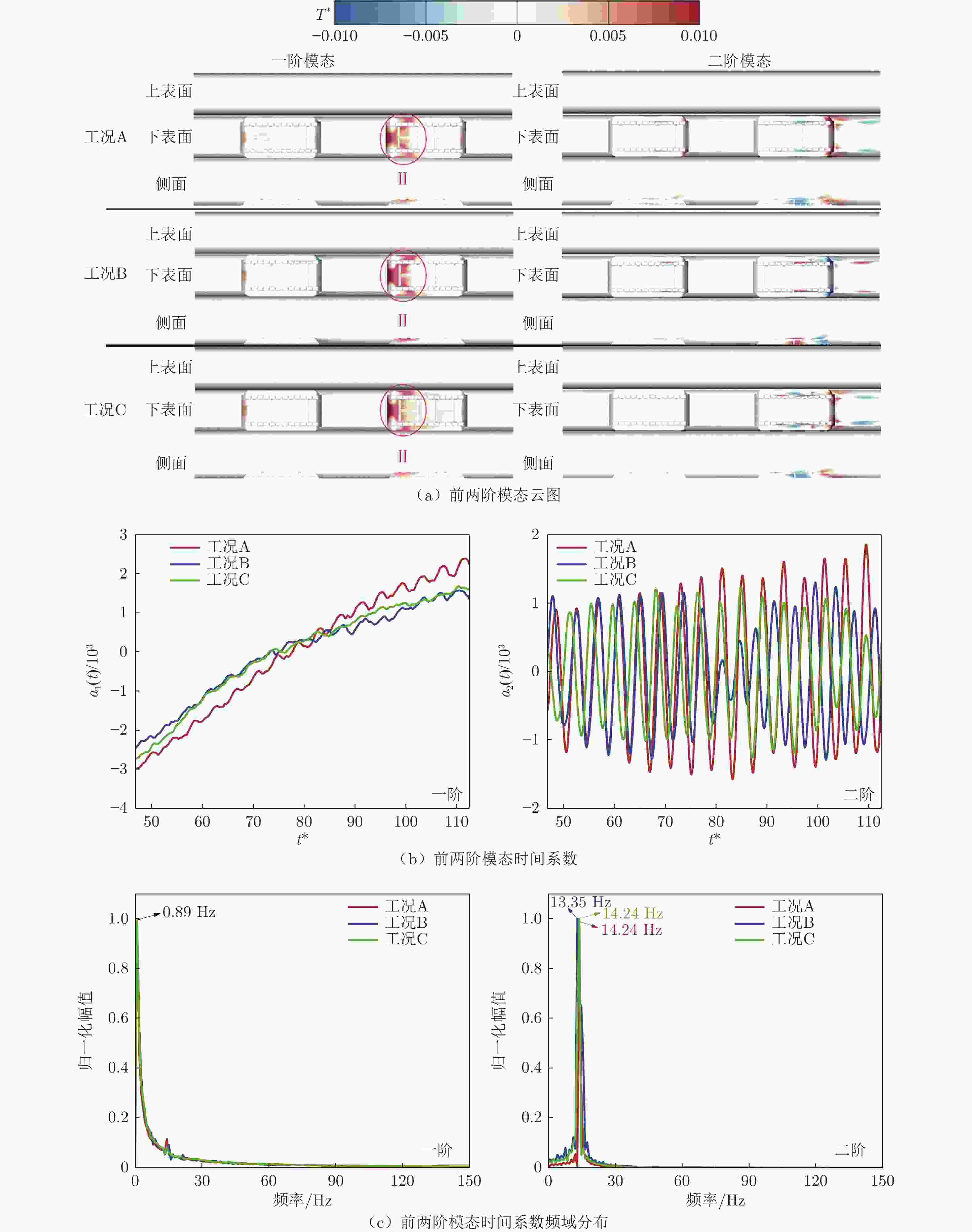
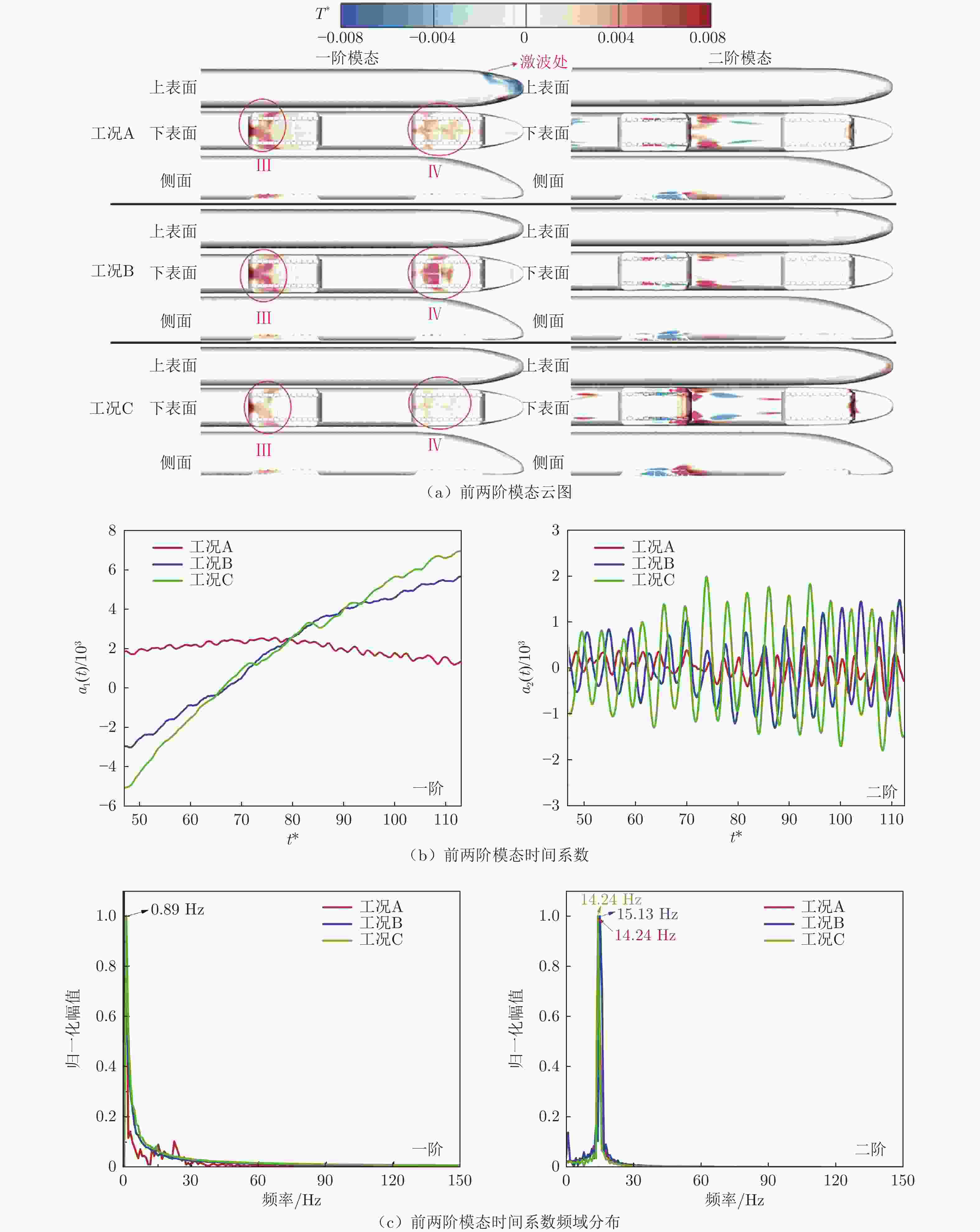
$k-\omega$ 湍流模型和IDDES方法,采用三维数值模型对800 km/h的真空管道磁浮交通系统在雍塞状态(阻塞比为0.3和0.2)和非雍塞状态(阻塞比为0.1)下进行瞬态模拟,得到列车车体热压载荷时均分布特征及其波动特性,并利用跨声速风洞凸块试验数据验证了数值方法的准确性。基于本征正交分解提取流场重要相干结构,识别列车表面载荷非定常较强区域,揭示其时空演化规律。研究结果表明:列车上表面载荷分布特征与拉瓦尔喷管相似,雍塞/非雍塞状态下载荷分布差异主要位于扩张段;列车下表面载荷分布因悬浮架腔体的截面突变而变得复杂,气流突入到第一个悬浮架腔体形成局部滞止点,造成车体压力大幅度振荡,同时热量在列车底部聚集,尾车下洗气流和上洗气流相互作用差异导致了雍塞/非雍塞状态下温度峰值的位置不同;列车表面压力非定常较强区域主要位于底部悬浮架处,且存在14 Hz的特征频率,雍塞状态下尾车激波处也是一个非定常源;中间车、尾车温度载荷一阶模态体现了热量累积过程。Abstract: Based on the SST$k-\omega$ turbulence model and the IDDES method, a three-dimensional numerical model was used to simulate the transient state of an evacuated tube maglev transport system at 800 km/h in the choked (blockage ratio of 0.3 and 0.2) and unchoked (blockage ratio of 0.1) states. The accuracy of the numerical method was verified using transonic wind tunnel bump test data. Additionally, the significant coherent structure of the flow field was extracted based on the proper orthogonal decomposition, the region with the strong unsteady load on the train surface was identified, and its space-time evolution law was revealed. The results show that the load distribution on the upper surface of the train is similar to that of the Laval nozzle, and the difference in load distribution between the chocked/unchoked conditions is mainly in the divergent section. The load distribution on the lower surface of the train becomes complex due to the abrupt change in the cross-section of the bogie cavity. The difference in the interaction between the upwash and downwash flow leads to different locations of the temperature peaks under the choked/unchoked conditions. The strong unsteady pressure region on the train surface is mainly located at the bottom bogie and has a characteristic frequency of 14 Hz. The tail car shock wave is also an unsteady source under choked conditions. The first-order modes of the middle and tail car temperature loads reflect the heat accumulation process. -
表 1 计算工况
Table 1. Calculation case
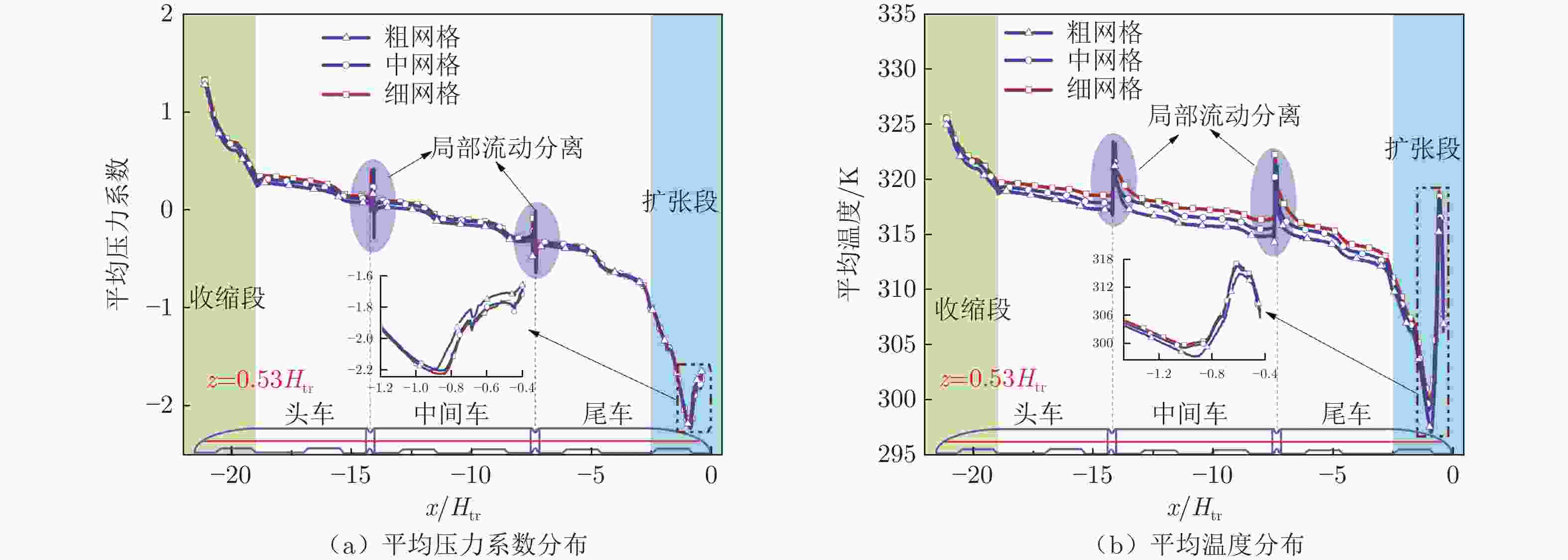
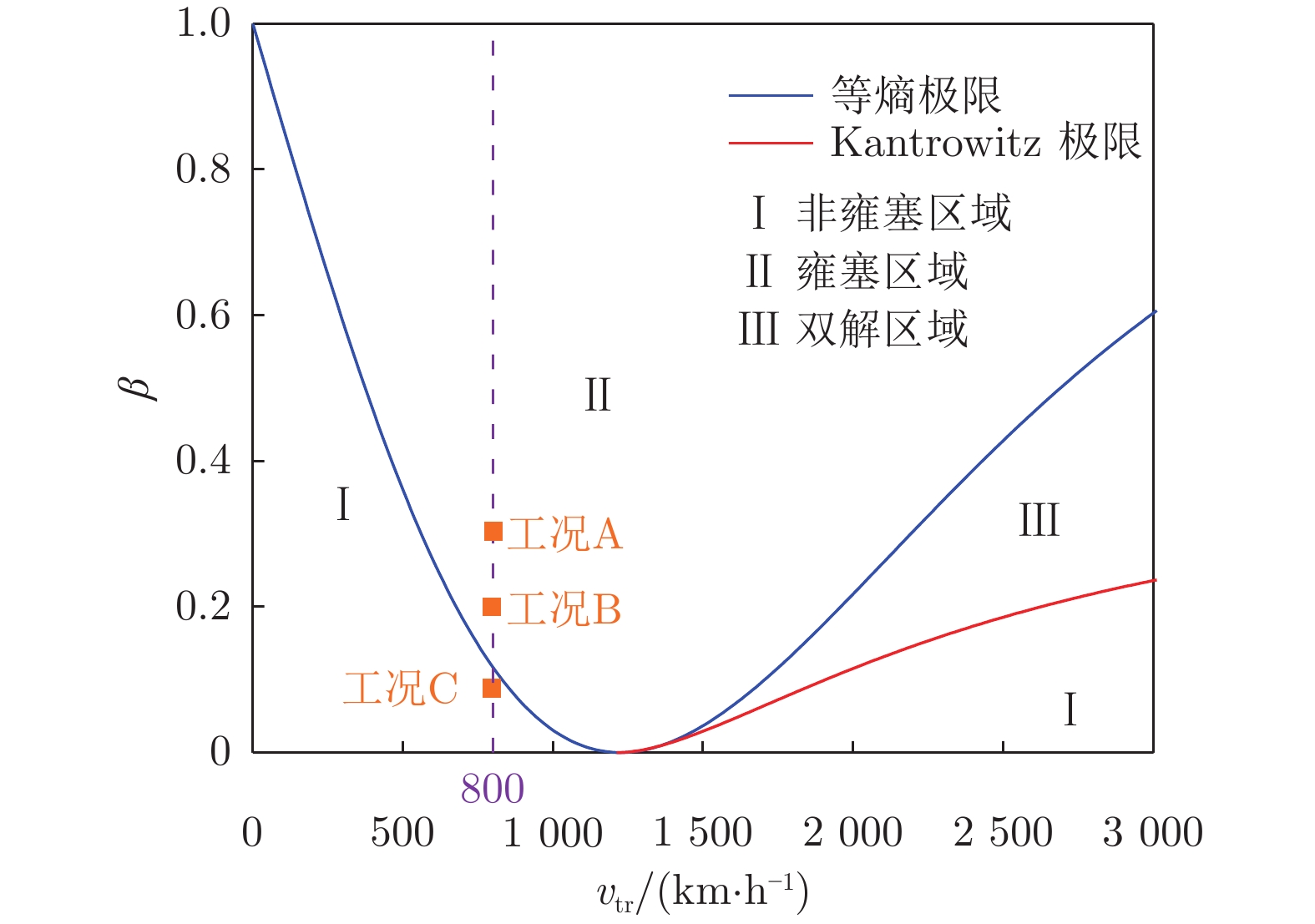
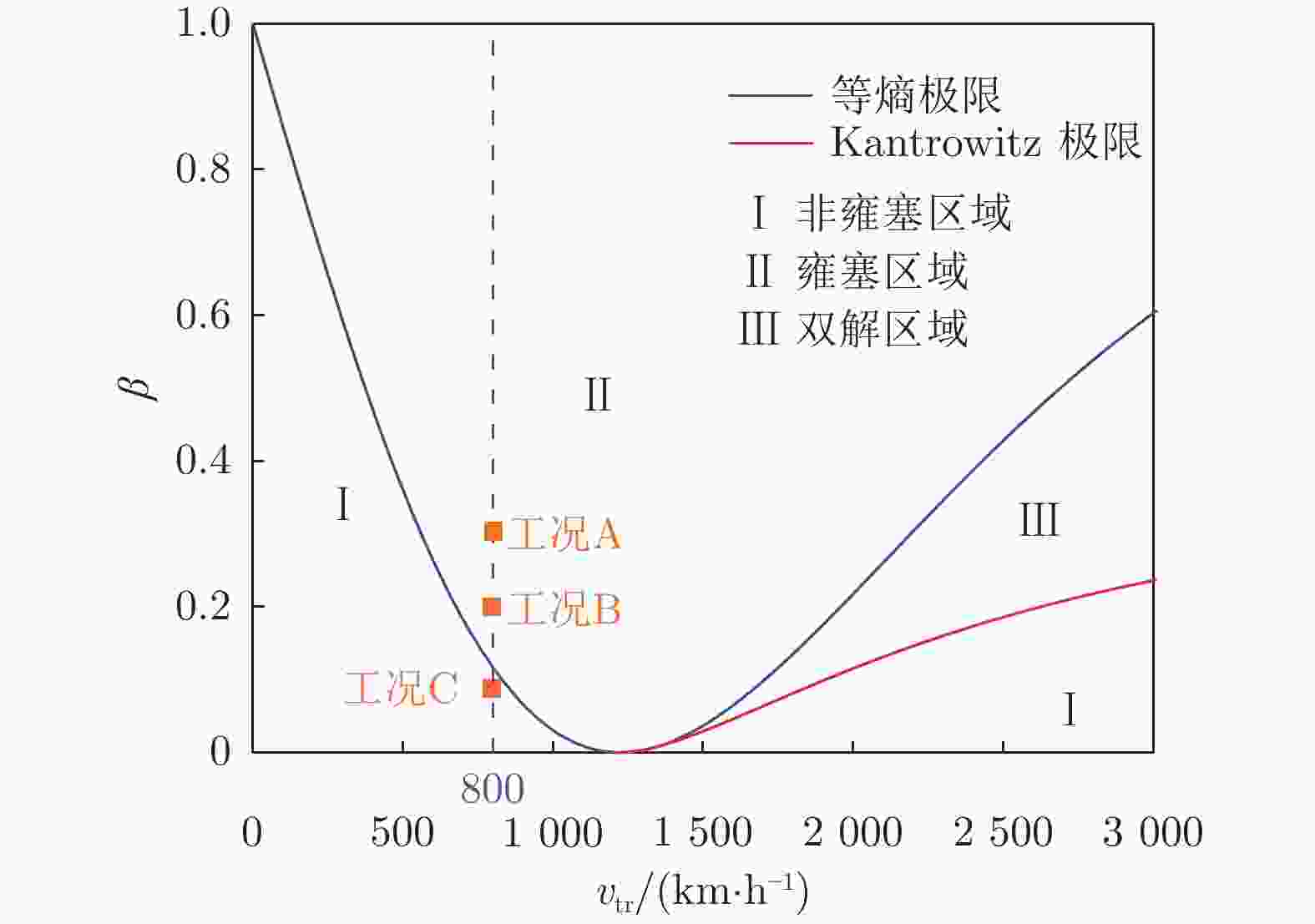
工况序号 列车速度/(km·h−1) 阻塞比 流动状态 A 800 0.3 雍塞 B 800 0.2 雍塞 C 800 0.1 非雍塞 表 2 用于网格独立性研究的3套网格分辨率
Table 2. Three sets of grid resolutions for grid independence studies
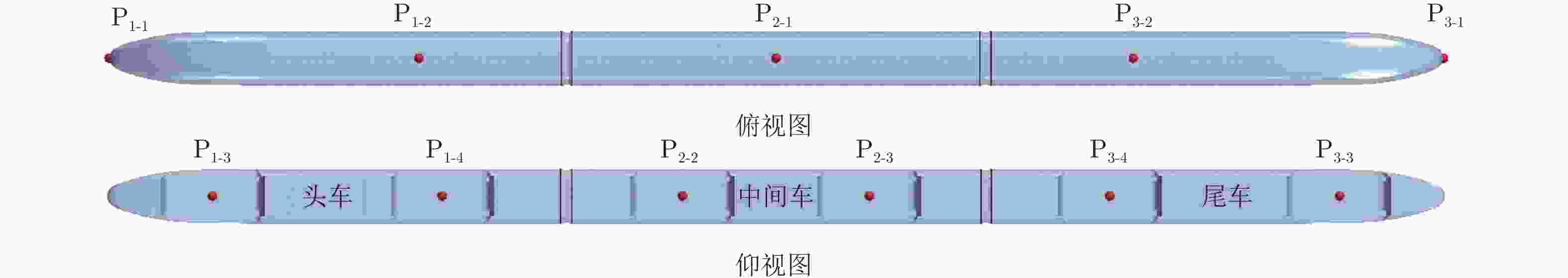
网格方案 最小网格尺寸 y+ 棱柱层数 网格总数 粗 0.0171Htr 1 22 1.42×107 中 0.0132Htr 1 22 2.44×107 细 0.0092Htr 1 26 5.01×107 表 3 列车表面监控点压力和温度最值及频域特性统计
Table 3. Statistics of pressure and temperature maxima and frequency domain characteristics at train surface monitoring points
车厢 监控点
序号工况A 工况B 工况C 压力系数 温度 压力系数 温度 压力系数 温度 最大值 最小值 主频
/Hz最大值
/K最小值
/K主频
/Hz最大值 最小值 主频
/Hz最大值
/K最小值
/K主频
/Hz最大值 最小值 主频
/Hz最大值
/K最小值
/K主频
/Hz头车 P1-1 1.98 1.92 0.89 330.38 328.81 0.89 1.57 1.49 0.89 321.64 320.09 0.89 1.29 1.15 0.89 316.30 313.43 0.89 P1-2 0.42 0.17 0.89 318.99 314.42 0.89 0.09 −0.28 0.89 311.63 309.04 0.89 −0.17 −0.41 0.89 305.47 303.84 0.89 P1-3 0.96 0.62 41.83 332.81 325.22 23.14 0.46 −0.01 38.27 321.92 314.32 38.27 0.03 −0.41 8.01 312.68 306.63 16.02 P1-4 0.44 0.15 23.14 338.57 330.56 23.14 0.14 −0.29 38.27 321.92 316.03 38.27 −0.10 −0.42 67.64 319.53 311.49 67.64 中间车 P2-1 −0.02 −0.17 14.24 314.78 311.56 14.24 −0.30 −0.49 0.89 306.97 305.06 0.89 −0.40 −0.48 0.89 303.46 301.34 0.89 P2-2 0.17 0 14.24 362.44 348.61 0.89 −0.09 −0.40 13.35 342.82 335.50 0.89 −0.31 −0.47 14.24 340.51 332.77 0.89 P2-3 −0.01 −0.16 14.24 382.14 354.89 0.89 −0.29 −0.52 0.89 364.70 347.24 0.89 −0.34 −0.48 14.24 370.86 346.76 0.89 尾车 P3-1 −1.36 −2.23 0.89 363.99 288.83 13.35 −0.72 −1.29 0.89 331.24 308.18 3.56 −0.10 −0.29 4.45 328.60 308.59 0.89 P3-2 −0.34 −0.52 14.24 312.42 307.73 14.24 −0.62 −0.71 13.35 305.54 301.72 0.89 −0.44 −0.52 18.69 303.69 301.15 0.89 P3-3 −1.20 −1.27 0.89 354.89 295.41 0.89 −1.07 −1.25 0.89 358.57 293.60 0.89 −0.41 −0.48 0.89 420.87 358.76 0.89 P3-4 −0.25 −0.40 14.24 389.36 348.36 0.89 −0.51 −0.67 15.13 379.84 338.82 0.89 −0.37 −0.51 14.24 390.29 348.19 0.89 -
[1] 邓自刚, 刘宗鑫, 李海涛, 等. 磁悬浮列车发展现状与展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(3): 455–474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001DENG Z G, LIU Z X, LI H T, et al. Development status and prospect of maglev train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 455–474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001 [2] VAN GOEVERDEN K, MILAKIS D, JANIC M, et al. Analysis and modelling of performances of the HL (Hyper-loop) transport system[J]. European Transport Research Review, 2018, 10(2): 41. doi: 10.1186/s12544-018-0312-x [3] 邓自刚, 张勇, 王博, 等. 真空管道运输系统发展现状及展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(5): 1063–1072. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20180204DENG Z G, ZHANG Y, WANG B, et al. Present situation and prospect of evacuated tube transportation system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(5): 1063–1072. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20180204 [4] SUI Y, NIU J Q, RICCO P, et al. Impact of vacuum degree on the aerodynamics of a high-speed train capsule running in a tube[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2021, 88: 108752. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2020.108752 [5] 黄尊地, 梁习锋, 常宁. 真空管道交通列车气动阻力数值分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2019, 55(8): 165–172. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.08.165HUANG Z D, LIANG X F, CHANG N. Numerical analysis of train aerodynamic drag of vacuum tube traffic[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(8): 165–172. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.08.165 [6] MA T H, HU X, WANG J K, et al. Effect of air pressure on aerodynamic characteristics of the HTS maglev running in a tube[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2021, 31(8): 0501004. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2021.3099770 [7] SUI Y, NIU J Q, YU Q J, et al. Numerical analysis of the aerothermodynamic behavior of a Hyperloop in choked flow[J]. Energy, 2021, 237: 121427. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.121427 [8] 张晓涵, 李田, 张继业, 等. 亚音速真空管道列车气动壅塞及激波现象[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(4): 182–190. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.04.182ZHANG X H, LI T, ZHANG J Y, et al. Aerodynamic choked flow and shock wave phenomena of subsonic evacuated tube train[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(4): 182–190. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.04.182 [9] HU X, DENG Z G, ZHANG W H. Effect of cross passage on aerodynamic characteristics of super-high-speed evacuated tube transportation[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2021, 211: 104562. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2021.104562 [10] ZHOU P, ZHANG J Y, LI T. Effects of blocking ratio and Mach number on aerodynamic characteristics of the eva-cuated tube train[J]. International Journal of Rail Tran-sportation, 2020, 8(1): 27–44. doi: 10.1080/23248378.2019.1675191 [11] 胡啸, 邓自刚, 张银龙, 等. 真空管道磁浮交通管内波系时空分布特征[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2022, 40(6): 146-154.HU X, DENG Z G, ZHANG Y L, et al. Characteristics of spatial and temporal distribution of wave system in eva-cuated tube maglev transportation[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2022, 40(6): 146-154. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2021.0242 [12] BAO S J, HU X, WANG J K, et al. Numerical study on the influence of initial ambient temperature on the aero-dynamic heating in the tube train system[J]. Advances in Aerodynamics, 2020, 2(1): 28. doi: 10.1186/s42774-020-00053-8 [13] 王成鹏, 杨锦富, 程川, 等. 超声速喷管起动过程激波结构演化特征[J]. 实验流体力学, 2019, 33(2): 11–16. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20180143WANG C P, YANG J F, CHENG C, et al. Research on evolution of starting shock in a supersonic nozzle[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 33(2): 11–16. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20180143 [14] LI T, SONG J, ZHANG X H, et al. Theoretical and numerical studies on compressible flow around a subsonic evacuated tube train[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C:Journal of Mechanical Engi-neering Science, 2022, 236(15): 8261–8271. doi: 10.1177/09544062221087826 [15] JANG K S, LE T T G, KIM J, et al. Effects of compressible flow phenomena on aerodynamic characteristics in Hyper-loop system[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 117: 106970. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.106970 [16] 侯自豪, 朱雨建, 薄靖龙, 等. 真空管道列车准一维气动特性[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(6): 119–129. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.06.119HOU Z H, ZHU Y J, BO J L, et al. Quasi-one-dimensional aerodynamic characteristics of tube train[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(6): 119–129. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.06.119 [17] HOU Z H, ZHU Y J, BO J L, et al. A quasi-one-dimensional study on global characteristics of tube train flows[J]. Phy-sics of Fluids, 2022, 34: 026104. doi: 10.1063/5.0080544 [18] YU Q J, YANG X F, NIU J Q, et al. Theoretical and numerical study of choking mechanism of fluid flow in Hyperloop system[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2022, 121: 107367. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2022.107367 [19] YU Q J, YANG X F, NIU J Q, et al. Aerodynamic thermal environment around transonic tube train in choked/un-choked flow[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2021, 92: 108890. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2021.108890 [20] 余秋君, 杨肖峰, 牛纪强, 等. 壅塞效应对低气压管道高速列车气动加热的影响[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2022, 43(1): 211–218.YU Q J, YANG X F, NIU J Q, et al. Choking effects on aerodynamic heating of high-speed train in the evacuated tube[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2022, 43(1): 211–218. [21] ZHONG S, QIAN B S, YANG M Z, et al. Investigation on flow field structure and aerodynamic load in vacuum tube transportation system[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2021, 215: 104681. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2021.104681 [22] HU X, DENG Z G, ZHANG J W, et al. Effect of tracks on the flow and heat transfer of supersonic evacuated tube maglev transportation[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2021, 107: 103413. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2021.103413 [23] BIZZOZERO M, SATO Y, SAYED M A. Aerodynamic study of a hyperloop pod equipped with compressor to overcome the Kantrowitz limit[J]. Journal of Wind Engi-neering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2021, 218: 104784. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2021.104784 [24] ZHOU K Y, DING G F, WANG Y M, et al. Aeroheating and aerodynamic performance of a transonic hyperloop pod with radial gap and axial channel: a contrastive study[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2021, 212: 104591. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2021.104591 [25] JIA W G, WANG K, CHENG A P, et al. Air flow and differential pressure characteristics in the vacuum tube transportation system based on pressure recycle ducts[J]. Vacuum, 2018, 150: 58–68. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.12.023 [26] 宋嘉源, 李田, 张晓涵, 等. 亚声速真空管道磁浮系统气动热特性研究[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2022, 40(2): 115–121. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2021.0227SONG J Y, LI T, ZHANG X H, et al. Research on aerodynamic and thermal characteristics of subsonic eva-cuated tube maglev system[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2022, 40(2): 115–121. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2021.0227 [27] 范孝华, 唐志共, 王刚, 等. 激波/湍流边界层干扰低频非定常性研究评述[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(1): 625917. doi: 10.7527/S10006-893.2021.25917FAN X H, TANG Z G, WANG G, et al. Review of low-frequency unsteadiness in shock wave/turbulent boundary layer interaction[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(1): 625917. doi: 10.7527/S10006-893.2021.25917 [28] 谢丹, 冀春秀, 景兴建. 高超声速典型弹道下的壁板热气动弹性动力学分析[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(11): 524843. doi: 10.7527/S10006-893.2021.24843XIE D, JI C X, JING X J. Dynamics analysis of panel aerothermoelasticity in typical hypersonic trajectories[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(11): 524843. doi: 10.7527/S10006-893.2021.24843 [29] 周伟, 李佳乐, 王兆华, 等. 高速列车底板铆钉结构的分区应力解算与气动疲劳评估[J]. 南京理工大学学报, 2022, 46(2): 127–134. doi: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2022.46.02.001ZHOU W, LI J L, WANG Z H, et al. Partitioned stress solution and aerodynamic fatigue assessment for rivet structure of high-speed train floor[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2022, 46(2): 127–134. doi: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2022.46.02.001 [30] 刘雯, 郭迪龙, 张子健, 等. 基于POD分解的高速列车尾流动力学特性研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2020, 42(9): 49–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.09.007LIU W, GUO D L, ZHANG Z J, et al. Study of dynamic characteristics in wake flow of high-speed train based on POD[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(9): 49–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.09.007 [31] ZHOU Z W, XIA C, DU X Z, et al. Impact of the isentropic and Kantrowitz limits on the aerodynamics of an evacuated tube transportation system[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2022, 34: 066103. doi: 10.1063/5.0090971 [32] OPGENOORD M M J, CAPLAN P C. Aerodynamic design of the hyperloop concept[J]. AIAA Journal, 2018, 56(11): 4261–4270. doi: 10.2514/1.J057103 [33] 丁叁叁, 姚拴宝, 陈大伟. 高速磁浮列车气动升力特性[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(8): 228–234. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.08.228DING S S, YAO S B, CHEN D W. Aerodynamic lift force of high-speed maglev train[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engi-neering, 2020, 56(8): 228–234. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.08.228 [34] 梅元贵, 李绵辉, 胡啸, 等. 时速600公里磁浮列车隧道初始压缩波洞内传播特征和洞口微气压波特征[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(4): 150–162. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.04.011MEI Y G, LI M H, HU X, et al. Propagation characteristics of initial compression wave in cave and portal micro-pressure waves characteristics when 600 km·h-1 maglev train entering tunnels[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(4): 150–162. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.04.011 [35] 郭婷, 夏超, 储世俊, 等. 不同转向架构型对高速列车列车风及非定常尾迹的影响[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2022, 40(2): 94–104. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2021.0239GUO T, XIA C, CHU S J, et al. Impact of different bogie configurations on slipstream and unsteady wake of a high-speed train[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2022, 40(2): 94–104. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2021.0239 [36] DONG T Y, MINELLI G, WANG J B, et al. The effect of ground clearance on the aerodynamics of a generic high-speed train[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2020, 95: 102990. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2020.102990 [37] INGER G, GENDT C, INGER G, et al. An experimental study of transonic shock/turbulent boundary layer interac-tion on a roughened surface[C]//Proc of the 35th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. 1997. doi: 10.2514/6.1997-65 [38] MULD T W, EFRAIMSSON G, HENNINGSON D S. Flow structures around a high-speed train extracted using Proper Orthogonal Decomposition and Dynamic Mode Decompo-sition[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2012, 57: 87–97. doi: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2011.12.012 [39] BELL J R, BURTON D, THOMPSON M C, et al. Flow topology and unsteady features of the wake of a generic high-speed train[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2016, 61: 168–183. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2015.11.009 [40] SIROVICH L. Turbulence and the dynamics of coherent structures. I. Coherent structures[J]. Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 1987, 45(3): 561–571. doi: 10.1090/qam/910462 [41] 王洪伟. 我所理解的流体力学[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2019. -









 下载:
下载: