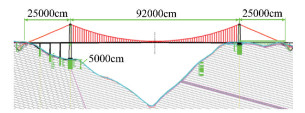
Scope effects of terrain models on wind properties design of a bridge located at mountainous area
-
摘要: 围绕某跨深切峡谷桥梁的设计风参数,按缩尺比1:1000的比例制作了4组不同规模的地形模型并展开风洞试验。与4组模型相对应的实际地形的投影面积分别为25、20、9和1km2。模型的地形跨度用峡谷的特征尺度进行了无量纲化。试验测试了沿峡谷走向的东南方向(SE)风向下桥址的平均风速分布、平均风迎角以及湍流特性。研究结果表明,对于桥位平均风速以及平均风迎角特性,从桥位往SE方向地形的无量纲跨度大于2.2后已足以得到稳定的测试结果;对于桥面高度处的湍流度,实际面积大于20km2、从桥位往SE方向地形的无量纲跨度大于3.7后的模型才能得到较稳定的测试结果。而对于湍流度剖面4组模型各不相同,没有收敛迹象,表明模型规模还不足以形成稳定结果。山区桥梁抗风研究中已广泛采用地形模型试验法,本文的试验研究结果定性表明地形模型规模的选取须审慎对待。Abstract: Aiming at the wind properties design of a bridge over a deep-cutting valley, 4 terrain models of different scopes are made for wind tunnel investigation, according to the scale ratio of 1:1000. The actual terrain areas covered by the four models are 25, 20, 9 and 1 square kilometers, resepectively. Moreover, the scope of the terrain models is normalized by the characterized dimension of the valley. In the wind tunnel experiment, the mean wind velocity, wind angles of attack and turbulence properties are measured with the wind direction that approximately parallel to the valley. The results indicate that, for the mean wind velocities and wind angles of attack, stable results are obtained when nondimensionalized distance from the bridge site to SE direction in the terrain model is greater than 2.2. For turbulence intensities at the bridge deck height, the two models whose nondimensionalized distance to SE direction is larger than 3.7 result in stable outcomes. However, the profiles of turbulence intensity differ significantly among the 4 models, which indicate that the scope of the models are not large enough as far as the profiles of turbulence intensity are concerned. Terrain model tests[KG(-0.14mm]have been adopted extensively for the wind-resistant design of long-span bridges which ocated at the mountainous terrain. The investigation of this study indicates qualitatively that the scope of a terrain model for this kind of task should be cautiously selected.
-
Key words:
- mountainous terrain /
- terrain model /
- scope /
- bridge /
- wind property
-
表 1 4组模型的地形跨度
Table 1. Terrain spans in the 4 models
模型规模 A B C D 南北方向跨度/km 5.0 5.0 3.0 1.0 东西方向跨度/km 5.0 4.0 3.0 1.0 -
[1] 中交公路规划设计研究院.公路桥梁抗风设计规范JTG/T D60-01-2004[S].北京: 人民交通出版社, 2004.China Communications Construction Company Highway Consultants Co., Ltd. Wind-resistant design specification for highway bridges: JTG/T D60-01-2004[S]. Beijing: China Communications Publishing & Media Management Co., Ltd. 2004. [2] Miller C A, Davenport A G. Guidelines for the calculation of wind speed-ups in complex terrain[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1998, 74-76:189-197. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(98)00016-6 [3] Sierputowski P, Ostrowski J, Cenedese A. Experimental study of wind flow over the model of a valley[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1995, 57(2-3):127-136. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(95)00009-G [4] Bullard J E, Wiggs G F S, Nash D J. Experimental study of wind directional variability in the vicinity of a model valley[J]. Geomorphology, 2000, 35(1-2):127-143. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(00)00033-7 [5] Takahashi T, Ohtsu T, Yassin M F, et al. Turbulence characteristics of wind over a hill with a rough surface[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2002, 90(12-15):1697-1906. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(02)00280-5 [6] Kondo K, Tsuchiya M, Sanada S. Evaluation of effect of micro-topography on design wind velocity[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2002, 90(12-15):1707-1718. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(02)00281-7 [7] Lubitz W D, White B R. Wind-tunnel and field investigation of the effect of local wind direction on speed-up over hills[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2007, 95(8):639-661. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2006.09.001 [8] Bowen A J. Modelling of strong wind flows over complex terrain at small geometric scales[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2003, 91(12-15):1859-1871. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2003.09.029 [9] Yamaguchi A, Ishihara T, Fujino Y. Experimental study of the wind flow in a coastal region of Japan[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2003, 91(1-2):247-264. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(02)00349-5 [10] 陈政清, 李春光, 张志田, 等.山区峡谷地带大跨度桥梁风场特性试验[J].实验流体力学, 2008, 22(3):54-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9897.2008.03.012Chen Z Q, Li C G, Zhang Z T, et al. Model test study of wind field characteristics of long-span bridge site in mountainous valley terrain[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2008, 22(3):54-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9897.2008.03.012 [11] 白桦, 李加武, 刘健新.西部河谷地区三水河桥址风场特性试验研究[J].振动与冲击, 2012, 31(14):74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2012.14.016Bai H, Li J W, Liu J X. Experimental study on wind field characteristics of Sanshui river bridge site located in west valley region[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(14):74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2012.14.016 [12] 张玥, 唐金旺, 周敉, 等.峡谷复杂地形风场空间分布特性试验研究[J].振动与冲击, 2016, 35(12):35-40. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zdycj201612006Zhang Y, Tang J W, Zhou M, et al. Experimental research on the spatial distribution characteristics of wind field in valley terrain[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(12):35-49. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zdycj201612006 [13] Li Y L, Hu P, Xu X Y, et al. Wind characteristics at bridge site in a deep-cutting gorge by wind tunnel test[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2017, 160:30-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2016.11.002 -








 下载:
下载: