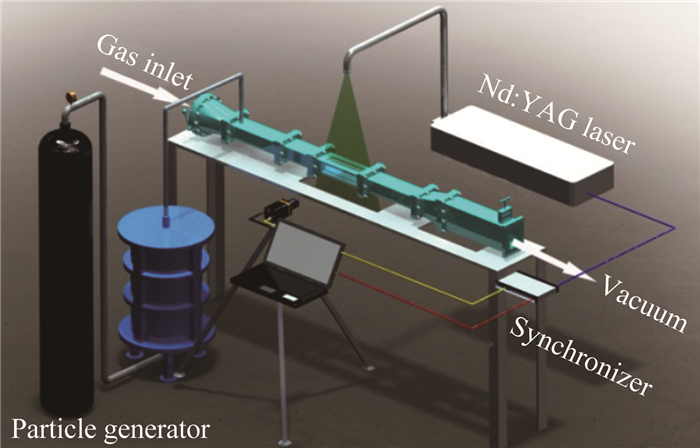
| [1] |
Curran E T, Stull F D. The utilization of supersonic combustion ramjet systems at low Mach numbers[R]. Aero Propulsion Lab, RTD-TDR-63-4097, 1964.
|
| [2] |
Curran E T, Heiser W H, Pratt D T. Fluid phenomena in scramjet combustion systems[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1996, 28(1):323-360. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fl.28.010196.001543
|
| [3] |
Matsuo K, Miyazato Y, Kim H D. Shock train and pseudo-shock phenomena in internal gas flows[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 1999, 35(1):33-100. doi: 10.1016/S0376-0421(98)00011-6
|
| [4] |
Carroll B F, Dutton J C. Turbulence phenomena in a multiple normal shock wave/turbulent boundary-layer interaction[J]. AIAA Journal, 1992, 30(1):43-48. doi: 10.2514/3.10880
|
| [5] |
Laurence S J, Karl S, Schramm J M, et al. Transient fluid-combustion phenomena in a model scramjet[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2013, 722(9):85-120. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f7b8f9e02efc49b03f83055f7c961375
|
| [6] |
Chang J, Wang L, Bao W, et al. Experimental investigation of hysteresis phenomenon for scramjet engine[J]. AIAA Journal, 2014, 52(2):447-451. doi: 10.2514/1.J052505
|
| [7] |
Fischer C, Olivier H. Experimental investigation of wall and total temperature influence on a shock train[J]. AIAA Journal, 2014, 52(4):757-766. doi: 10.2514/1.J052599
|
| [8] |
Fotia M L, Driscoll J F. Isolator-combustor interactions in a direct-connect ramjet-scramjet experiment[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2012, 28(1):83-95. doi: 10.2514/1.B34367
|
| [9] |
Grzona A, Olivier H. Shock train generated turbulence inside a nozzle with a small opening angle[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2011, 51(3):621-639. doi: 10.1007/s00348-011-1083-5
|
| [10] |
Tu Q, Segal C. Isolator/combustion chamber interactions during supersonic combustion[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2010, 26(1):182-186. doi: 10.2514/1.46156
|
| [11] |
Le D B, Goyne C P, Krauss R H, et al. Experimental study of a dual-mode scramjet isolator[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2008, 24(5):1050-1057. doi: 10.2514/1.32591
|
| [12] |
Wagner J L, Yuceil K B, Valdivia A, et al. Experimental investigation of unstart in an inlet/isolator model in Mach 5 flow[J]. AIAA Journal, 2009, 47(6):1528-1542. doi: 10.2514/1.40966
|
| [13] |
Wagner J L, Yuceil K B, Clemens N T. Velocimetry measurements of unstart of an inlet-isolator model in Mach 5 flow[J]. AIAA Journal, 2010, 48(9):1875-1888. doi: 10.2514/1.J050037
|
| [14] |
Srikant S, Wagner J L, Valdivia A, et al. Unstart detection in a simplified-geometry hypersonic inlet-isolator flow[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2010, 26(5):1059-1071. doi: 10.2514/1.46937
|
| [15] |
Donbar J M, Linn G J, Srikant S, et al. High-frequency pressure measurements for unstart detection in scramjet isolators[C]//Proc of 46th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit. 2010.
|
| [16] |
Donbar J M, Brown M S, Linn G J, et al. Simultaneous high-frequency pressure and TDLAS measurements in a small-scale axisymmetric isolator with bleed[R]. AIAA-2012-0331, 2012.
|
| [17] |
Pettinari S, Corradini M L, Serrani A. Detection of scramjet unstart in a hypersonic vehicle model[C]//Proc of American Control Conference Fairmont Queen Elizabeth. 2012.
|
| [18] |
Chang J, Zheng R, Wang L, et al. Backpressure unstart detection for a scramjet inlet based on information fusion[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2014, 95(1):1-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0232260505/
|
| [19] |
Chen Z, Yi S H, Zhu Y Z, et al. Investigation on flows in a supersonic isolator with an adjustable cowl convergence angle[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2014, 52(1):182-190. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3563aa5f627818bf84c2fe94fa1a78dd
|
| [20] |
Le D B, Goyne C P, Krauss R H. Shock train leading-edge detection in a dual-mode scramjet[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2008, 24(5):1035-1041. doi: 10.2514/1.32592
|
| [21] |
Hutzel J R, Decker D D, Cobbz R G, et al. Scramjet isolator shock train location techniques[C]//Proc of 49th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. 2011.
|
| [22] |
Hutzel J R, Decker D D, Donbar J M. Scramjet isolator shock-train leading-edge location modeling[R]. AIAA-2011-2223, 2011.
|
| [23] |
Weiss A, Olivier H. Behaviour of a shock train under the influence of boundary-layer suction by a normal slot[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2012, 52(2):273-287. doi: 10.1007/s00348-011-1211-2
|
| [24] |
Hu J, Chang J, Qin B, et al. Scramjet isolator shock-train leading-edge position modeling based on equilibrium manifold[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2013, 28(2):04014064. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5371b57d7d7ca0ee5835efe7e04404fa
|
| [25] |
Hutchins K E, Akella M R, Clemens N T, et al. Experimental identification of transient dynamics for supersonic inlet unstart[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2014, 30(6):1-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b99e6183e76c87ebdfb6cb64a3fa397b
|
| [26] |
Valdivia A, Yuceil K B, WagneJ L, et al. Control of supersonic inlet-isolator unstart using active and passive vortex generators[J]. AIAA Journal, 2014, 52(6):1207-1218. doi: 10.2514/1.J052214
|
| [27] |
Geerts J S, Yu K H. Shock train/Boundary-Layer interaction in rectangular isolators[J]. AIAA Journal, 2016, 54(11):3450-3464 doi: 10.2514/1.J054917
|
| [28] |
Geerts J S, Yu K H. Systematic application of background-oriented schlieren for isolator shock train visualization[J]. AIAA Journal, 2017, 55(4):1105-1117. doi: 10.2514/1.J054991
|
| [29] |
Fan X Q, Xiong B, Wang Y, et al. Self-excited and forced oscillation of a shock train in a rectangular isolator at Mach 3[C]//Proc of 21st AIAA International Space Plane and Hypersonics Technologies Conference. 2017.
|
| [30] |
Xiong B, Wang Z G, Fan X Q, et al. Response of shock train to high-frequency fluctuating backpressure in an isolator[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2017, 33(1):1-9. doi: 10.2514/1.B36521
|








 下载:
下载: