On complete rebound of liquid droplets impacting on soft hydrophobic surfaces
-
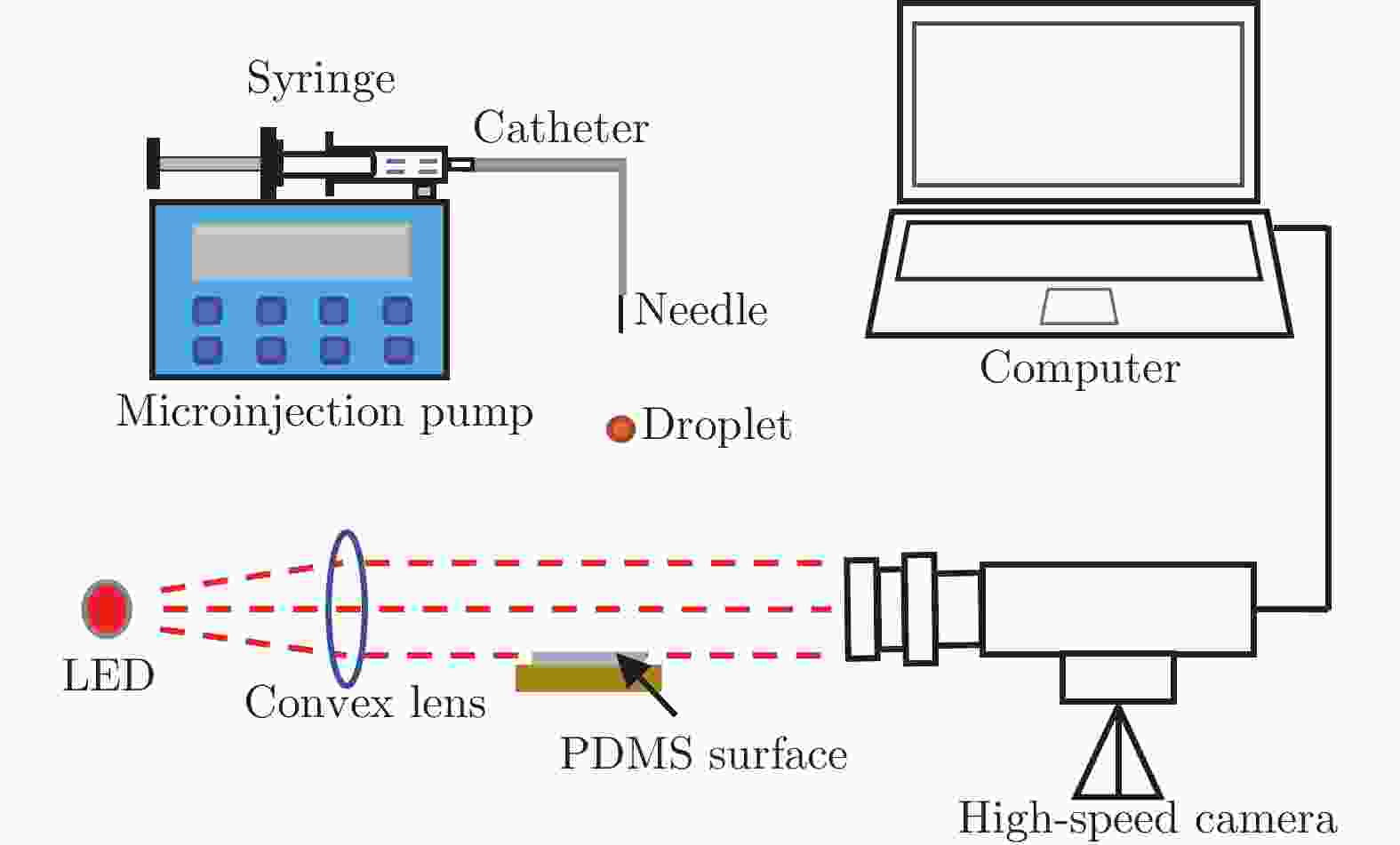
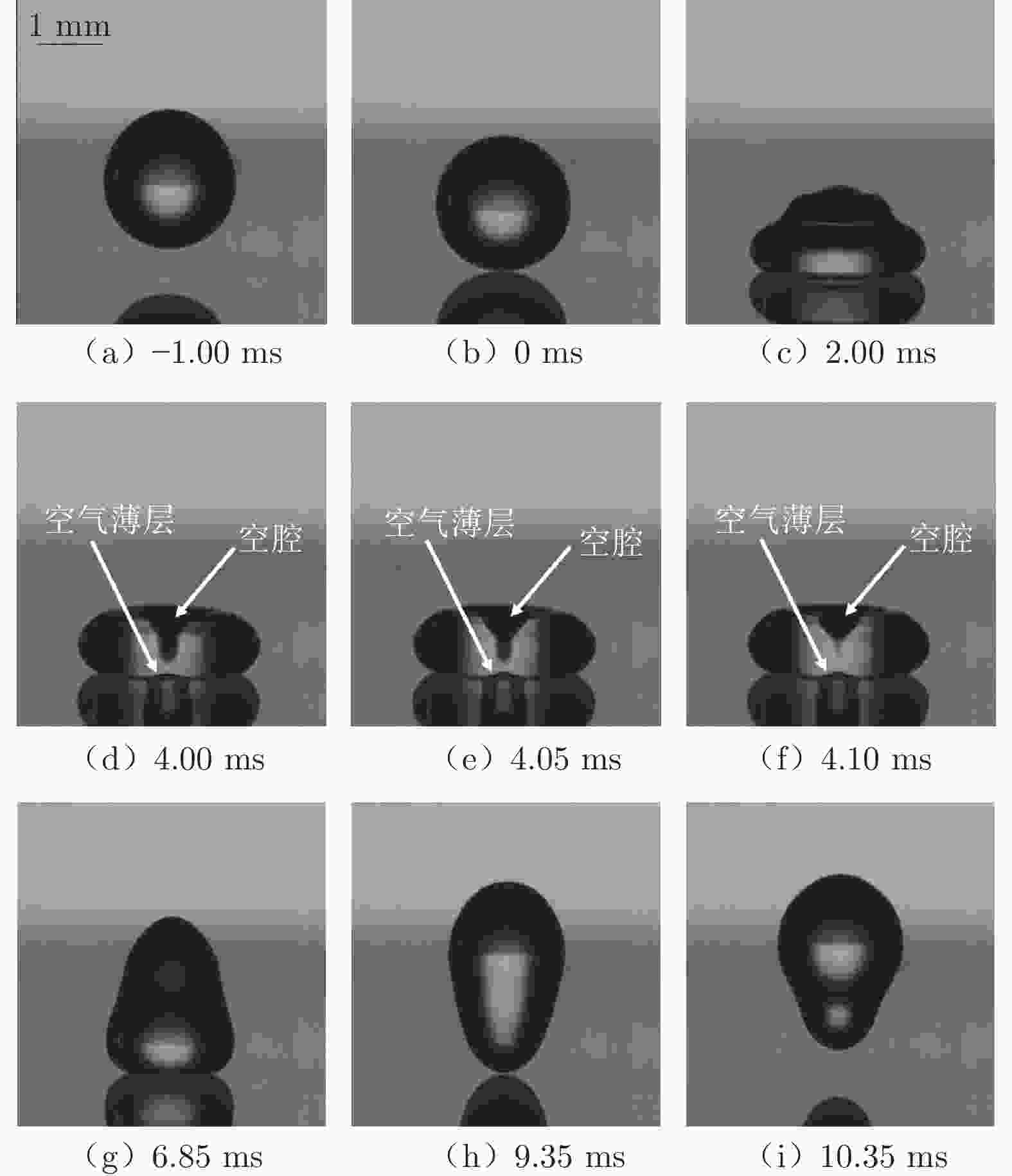
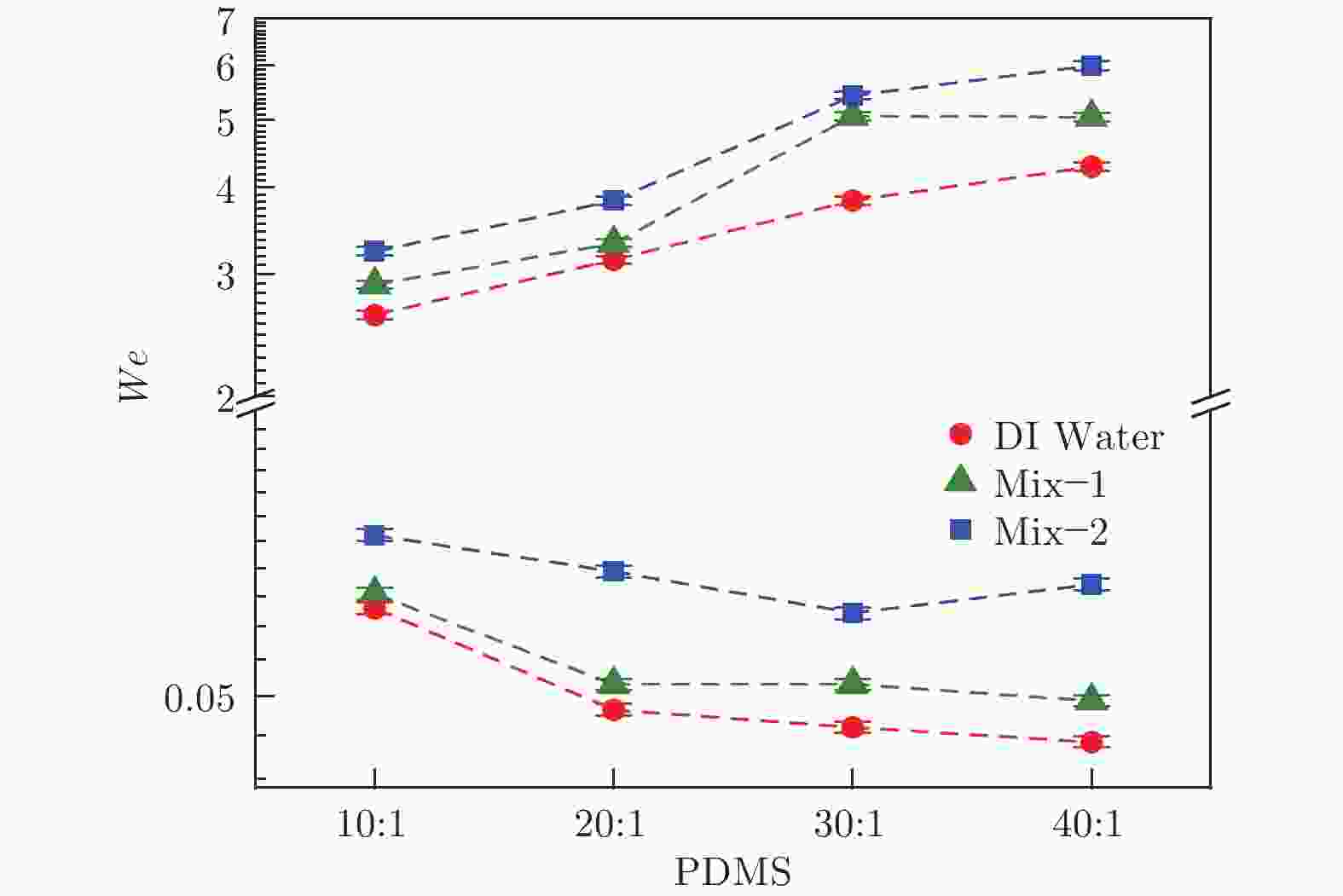
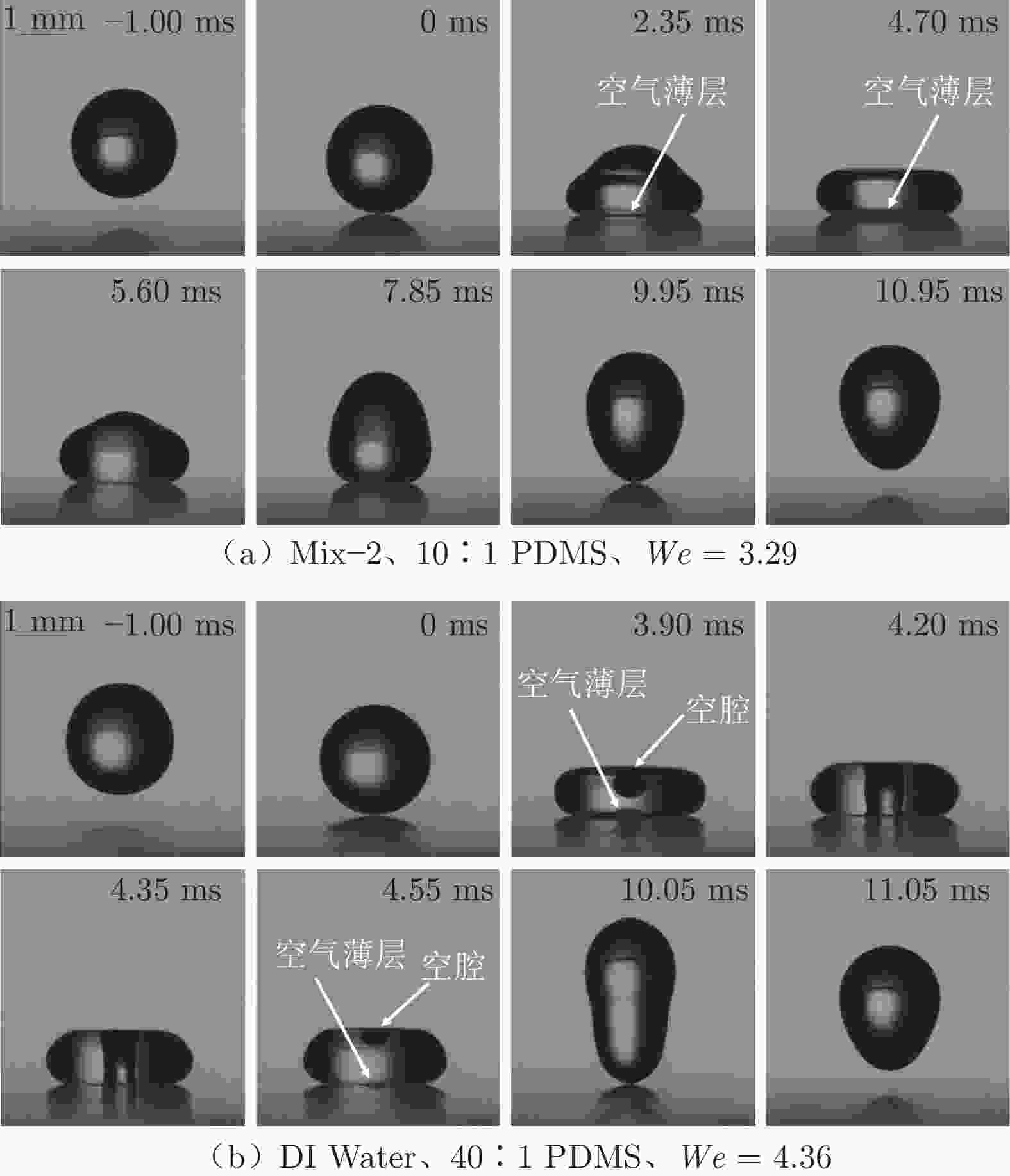
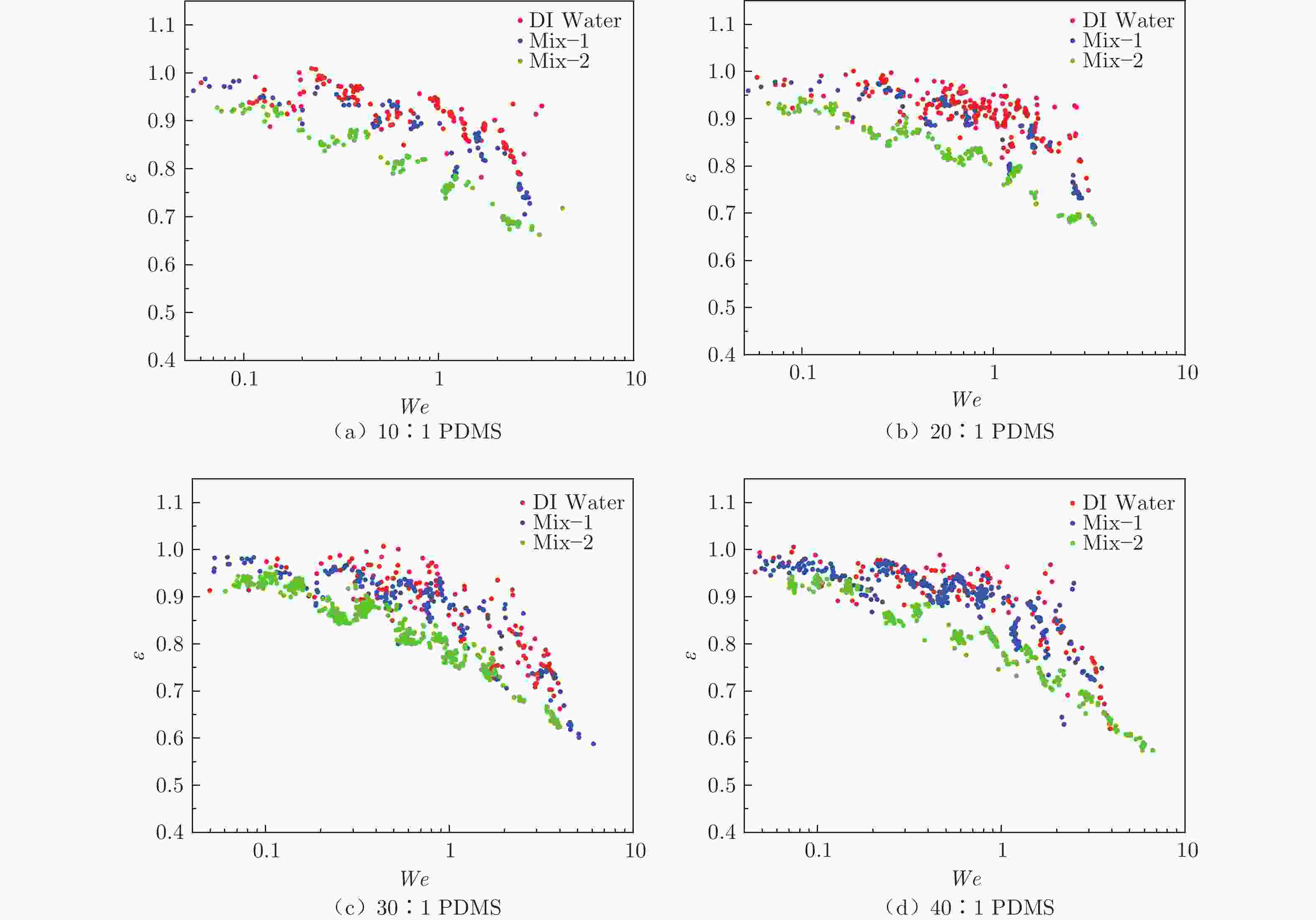
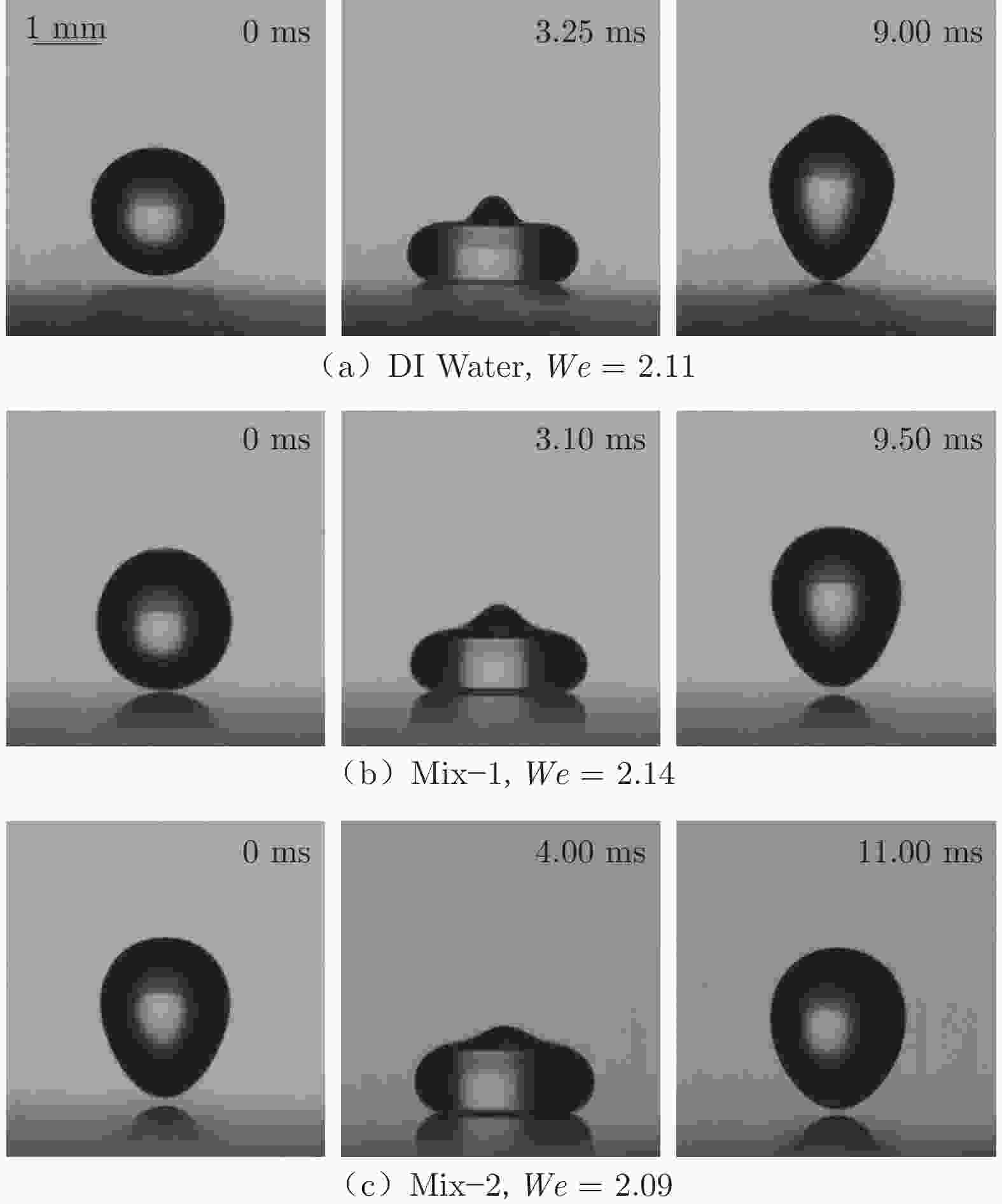
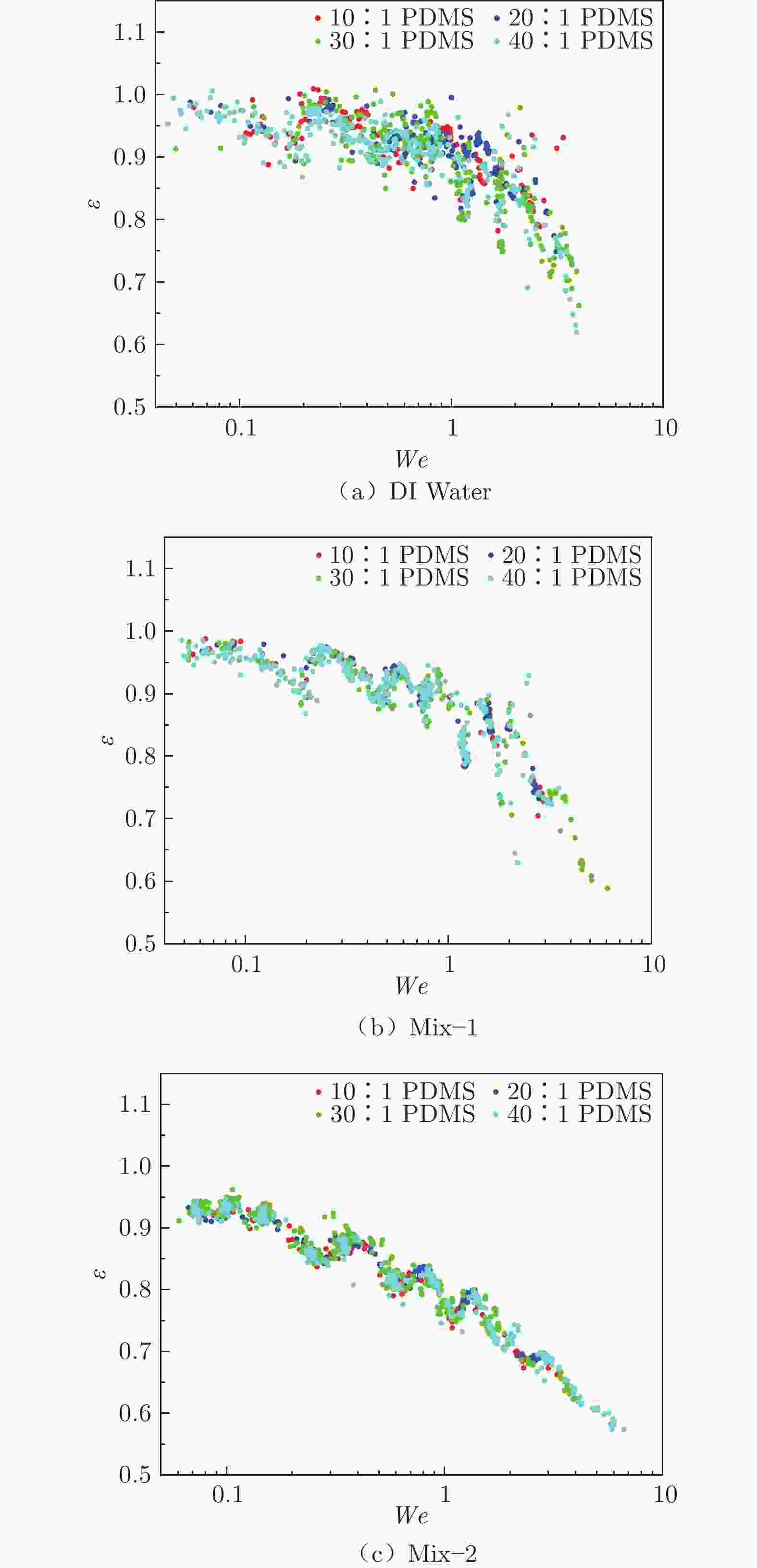
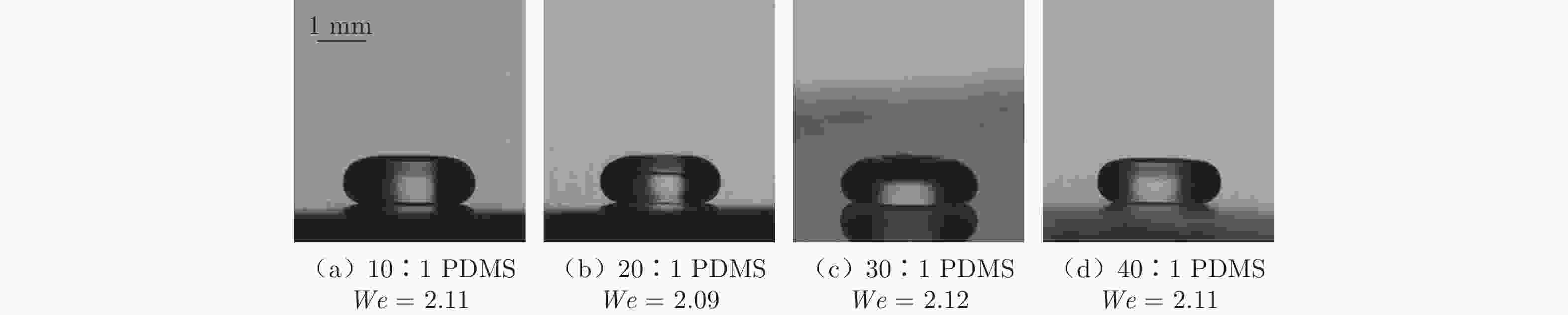
摘要: 采用高速摄影与图像识别技术,研究了不同黏性液滴撞击不同弹性模量的柔性疏水材料(PDMS)表面后的完全反弹过程,获得了液滴黏性和柔性疏水材料弹性模量对液滴发生完全反弹的韦伯数区间和反弹恢复系数的影响规律。结果表明:由于液滴黏性对液滴铺展过程的速度影响及其所导致的黏性能量耗散差异,当液滴黏性增大时,液滴撞击PDMS表面后发生完全反弹的最大/最小韦伯数均增大、反弹恢复系数减小;随着PDMS弹性模量的降低,液滴撞击PDMS表面后发生完全反弹的最大韦伯数增大、最小韦伯数减小,PDMS弹性模量对反弹恢复系数无明显影响。Abstract: With the method of high-speed camera and image recognition, the complete rebound of the liquid droplet with different viscosity impacting on the surface of the soft hydrophobic material (PDMS) with different elastic modulus was obtained. The influence curves of liquid viscosity and PDMS elastic modulus on the rebound Weber number and recovery coefficient of the droplet were also plotted. Due to the influence of liquid viscosity on the spreading process and viscous energy dissipation, the maximum and minimum Weber numbers of droplet complete rebound on PDMS surfaces increase with the increase of droplet viscosity, and the rebound recovery coefficient gradually decreases. With the decrease of the elastic modulus of PDMS, the maximum Weber number of droplet complete rebound on PDMS surface increases and the minimum Weber number decreases, and the elastic modulus of PDMS has no significant effect on the rebound recovery coefficient.
-
Key words:
- droplet /
- PDMS /
- complete rebound /
- viscosity coefficient /
- Weber number /
- rebound recovery coefficient
-
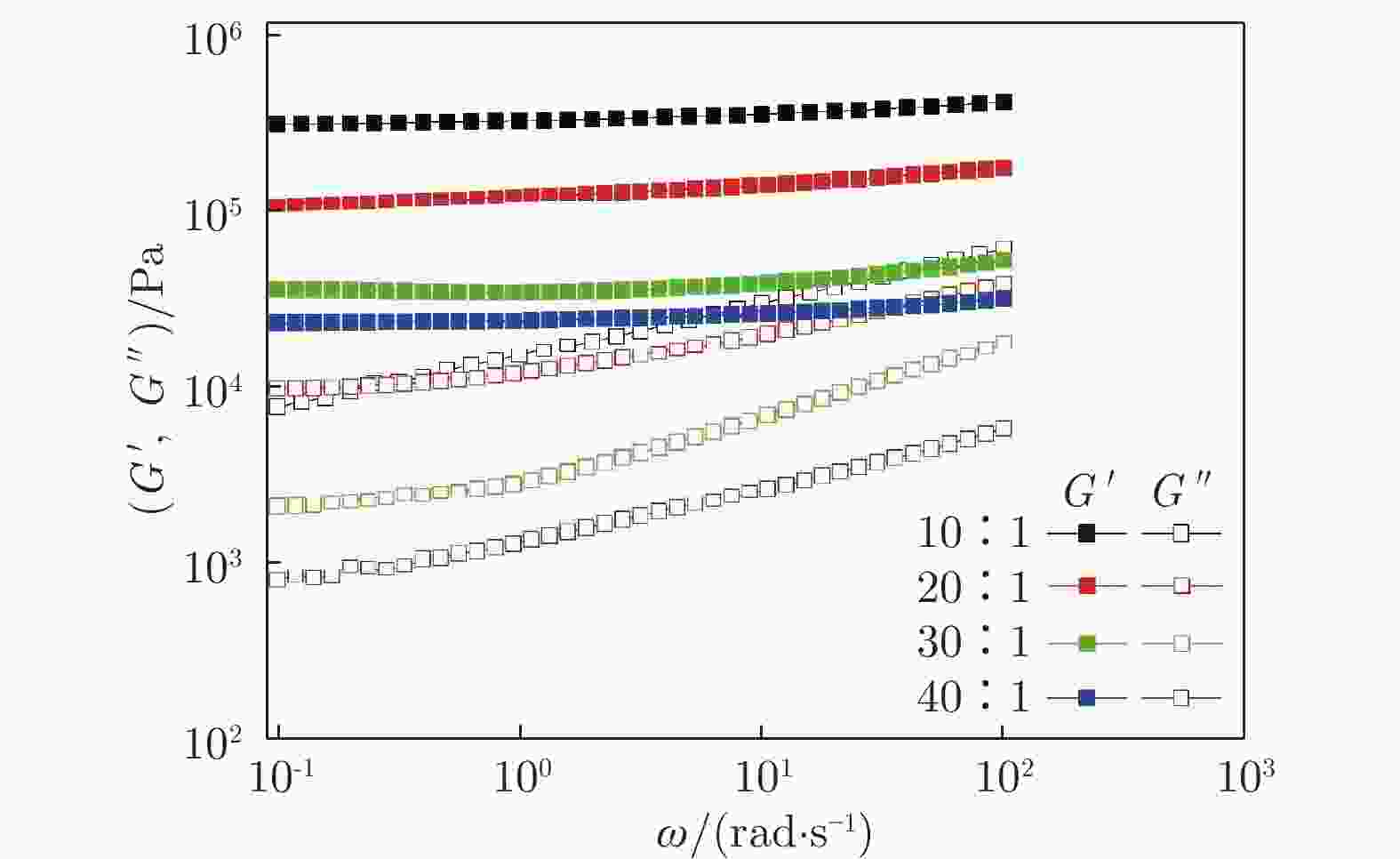
表 1 PDMS样品力学参数(ω = 1 rad/s)
Table 1. Elastic modulus of PDMS(ω = 1 rad/s)
No. Ratio $ G' $/kPa $ G'' $/kPa 1 10∶1 320.00 14.90 2 20∶1 120.00 11.70 3 30∶1 34.20 2.82 4 40∶1 24.00 1.29 表 2 实验液滴的基本参数
Table 2. Parameters of liquid droplets
No. Liquid
dropletsGlycerol
/(wt%)$ \gamma $
/(mN·m−1)$ \rho $
/(kg·m−3)$ \mu $
/(mPa·s)1 DI Water 0 72.1 998 1.01 2 Mix–1 30 71.7 1056 2.50 3 Mix–2 60 68.8 1150 10.8 -
[1] PARK B K, KIM D, JEONG S, et al. Direct writing of copper conductive patterns by ink-jet printing[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(19): 7706–7711. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2006.11.142 [2] JIA W, QIU H H. Experimental investigation of droplet dynamics and heat transfer in spray cooling[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2003, 27(7): 829–838. doi: 10.1016/S0894-1777(03)00015-3 [3] KREDER M J, ALVARENGA J, KIM P, et al. Design of anti-icing surfaces: smooth, textured or slippery?[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2016, 1: 15003. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2015.3 [4] GIBBS J L, PETERS T M, HECK L P. Comparison of droplet size, coverage, and drift potential from UAV application methods and ground application methods on row crops[J]. Transactions of the ASABE, 2021, 64(3): 819–828. doi: 10.13031/trans.14121 [5] REZAEI M, NETZ R R. Airborne virus transmission via respiratory droplets: effects of droplet evaporation and sedimentation[J]. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2021, 55: 101471. doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2021.101471 [6] COMPTON B G, LEWIS J A. 3D-printing of lightweight cellular composites[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(34): 5930–5935. doi: 10.1002/adma.201401804 [7] RIOBOO R, MARENGO M, TROPEA C. Outcomes from a drop impact on solid surfaces[J]. Atomization and Sprays, 2001, 11(2): 155–166. doi: 10.1615/atomizspr.v11.i2.40 [8] ANTONINI C, VILLA F, BERNAGOZZI I, et al. Drop rebound after impact: the role of the receding contact angle[J]. Langmuir: the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids, 2013, 29(52): 16045–16050. doi: 10.1021/la4012372 [9] BARTOLO D, BOUAMRIRENE F, VERNEUIL E, et al. Bouncing or sticky droplets: Impalement transitions on superhydrophobic micropatterned surfaces[J]. Europhysics Letters (EPL), 2006, 74(2): 299–305. doi: 10.1209/epl/i2005-10522-3 [10] OKUMURA K, CHEVY F, RICHARD D, et al. Water spring: a model for bouncing drops[J]. Europhysics Letters, 2003, 62(2): 237–243. doi: 10.1209/epl/i2003-00340-1 [11] RICHARD D, QUÉRÉ D. Bouncing water drops[J]. Europhysics Letters, 2000, 50(6): 769–775. doi: 10.1209/epl/i2000-00547-6 [12] JUNG Y C, BHUSHAN B. Dynamic effects of bouncing water droplets on superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Langmuir: the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids, 2008, 24(12): 6262–6269. doi: 10.1021/la8003504 [13] REYSSAT M, PÉPIN A, MARTY F, et al. Bouncing transitions on microtextured materials[J]. Europhysics Letters, 2006, 74(2): 306–312. doi: 10.1209/epl/i2005-10523-2 [14] RIOBOO R, VOUÉ M, VAILLANT A, et al. Drop impact on porous superhydrophobic polymer surfaces[J]. Langmuir: the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids, 2008, 24(24): 14074–14077. doi: 10.1021/la802897g [15] CHEN L Q, BONACCURSO E, DENG P G, et al. Droplet impact on soft viscoelastic surfaces[J]. Physical Review E, 2016, 94(6): 063117. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.94.063117 [16] CHEN L Q, LI Z G. Bouncing droplets on nonsuper-hydrophobic surfaces[J]. Physical Review E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2010, 82(1 Pt 2): 016308. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.82.016308 [17] CHEN L Q, WU J, LI Z G, et al. Evolution of entrapped air under bouncing droplets on viscoelastic surfaces[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2011, 384(1-3): 726–732. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.05.046 [18] LEE J B, DOS SANTOS S, ANTONINI C. Water touch-and-bounce from a soft viscoelastic substrate: wetting, dewetting, and rebound on bitumen[J]. Langmuir: the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids, 2016, 32(32): 8245–8254. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b01796 [19] 杨磊, 杨向龙, 王甫军. 液滴撞击柔性材料表面铺展特性的实验研究[J]. 实验流体力学, 2019, 33(3): 83–89. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20180086YANG L, YANG X L, WANG F J. On the maximum spreading of liquid droplets impacting on soft surfaces[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 33(3): 83–89. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20180086 [20] KOLINSKI J M, MAHADEVAN L, RUBINSTEIN S M. Drops can bounce from perfectly hydrophilic surfaces[J]. Europhysics Letters, 2014, 108(2): 24001. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/108/24001 -







 下载:
下载: