Investigation of acoustic liner vibroacoustic response and its influence on impedance
-
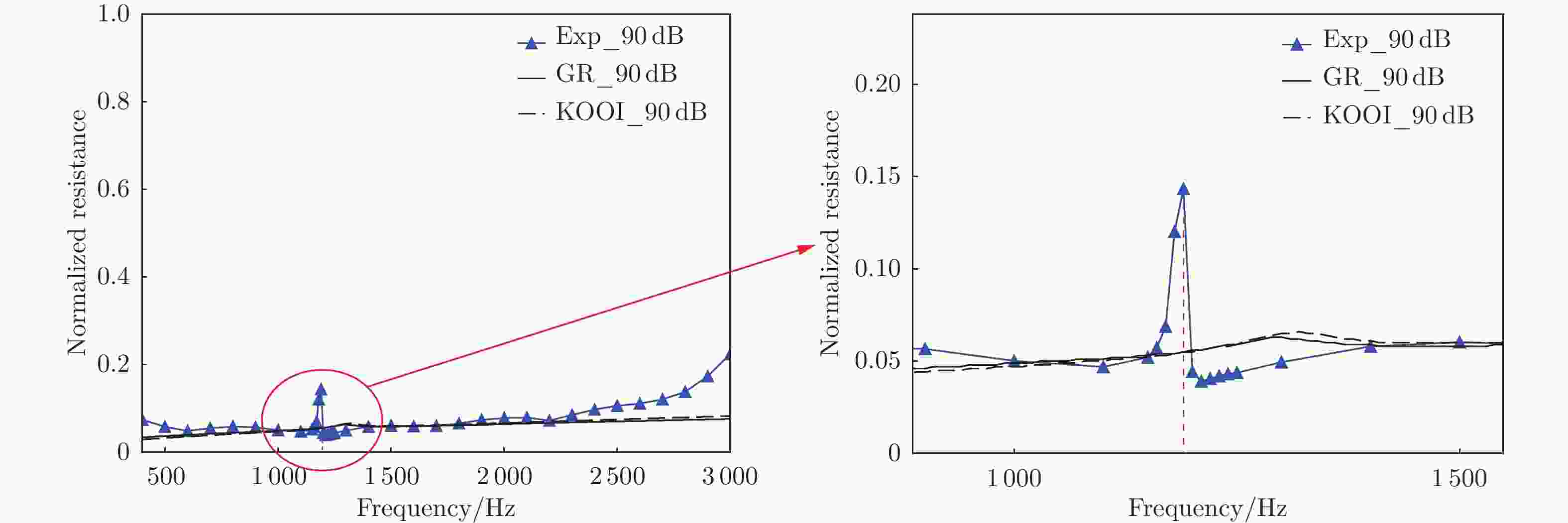
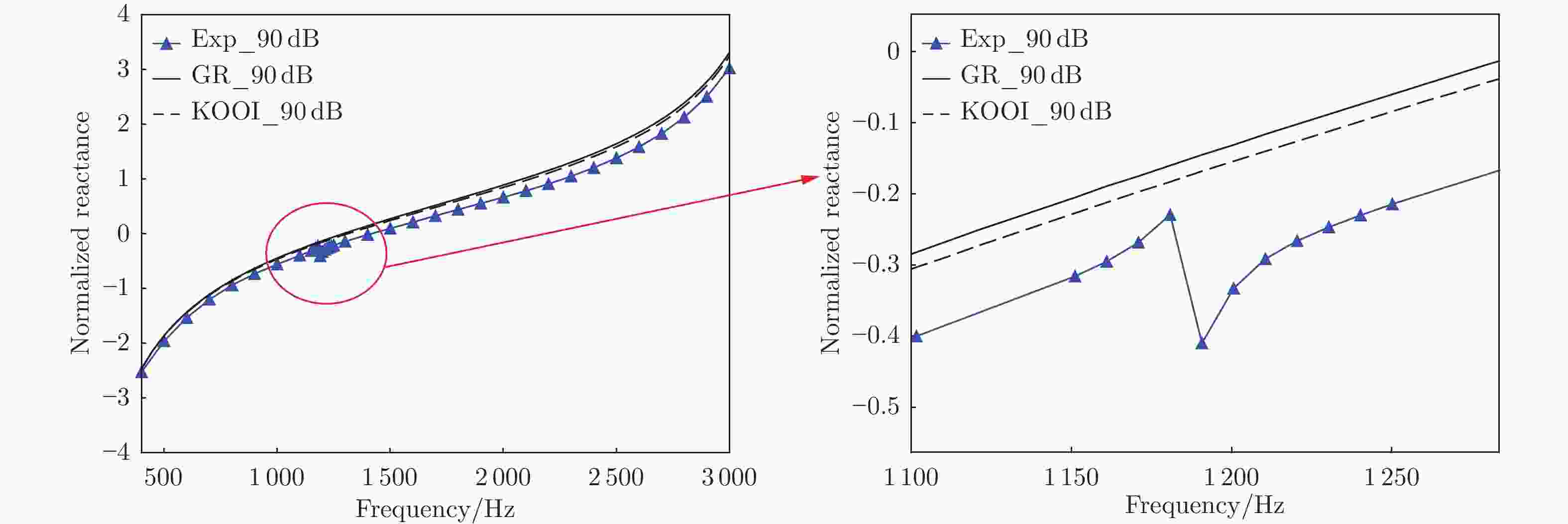
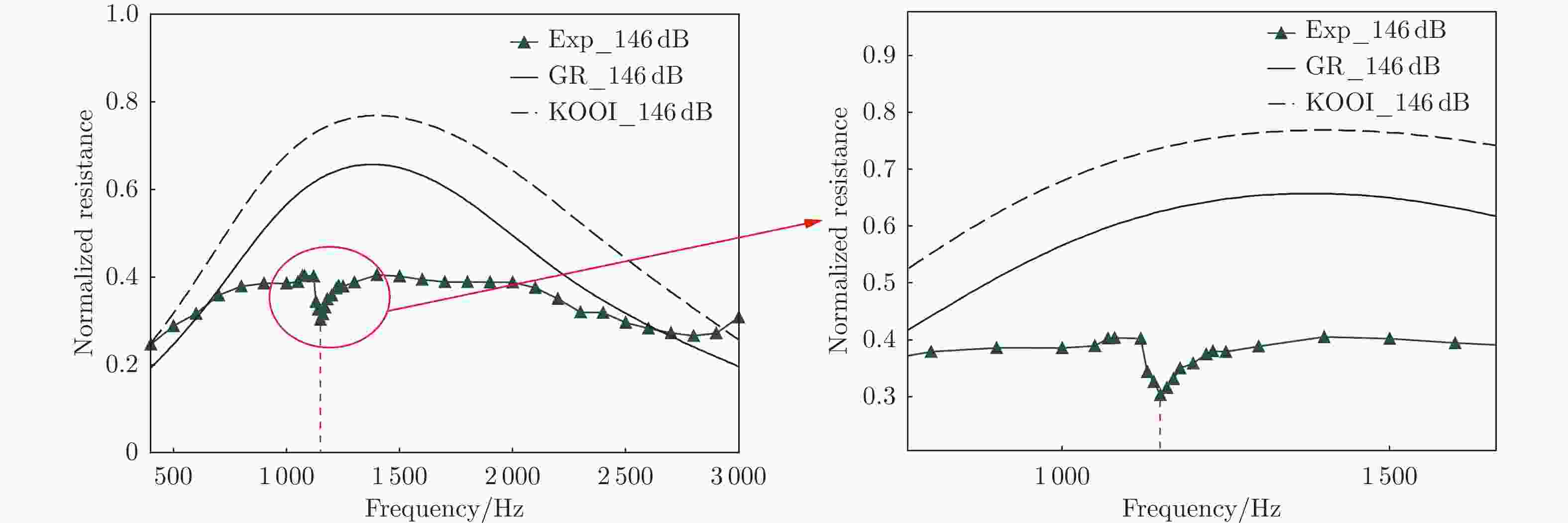
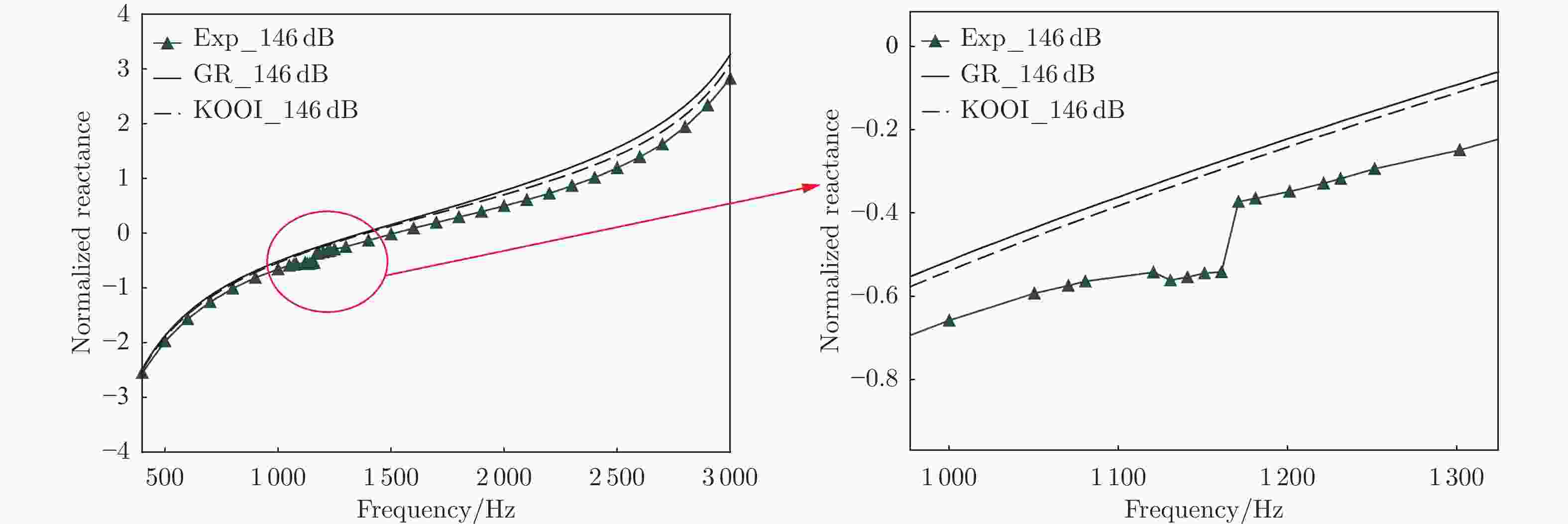
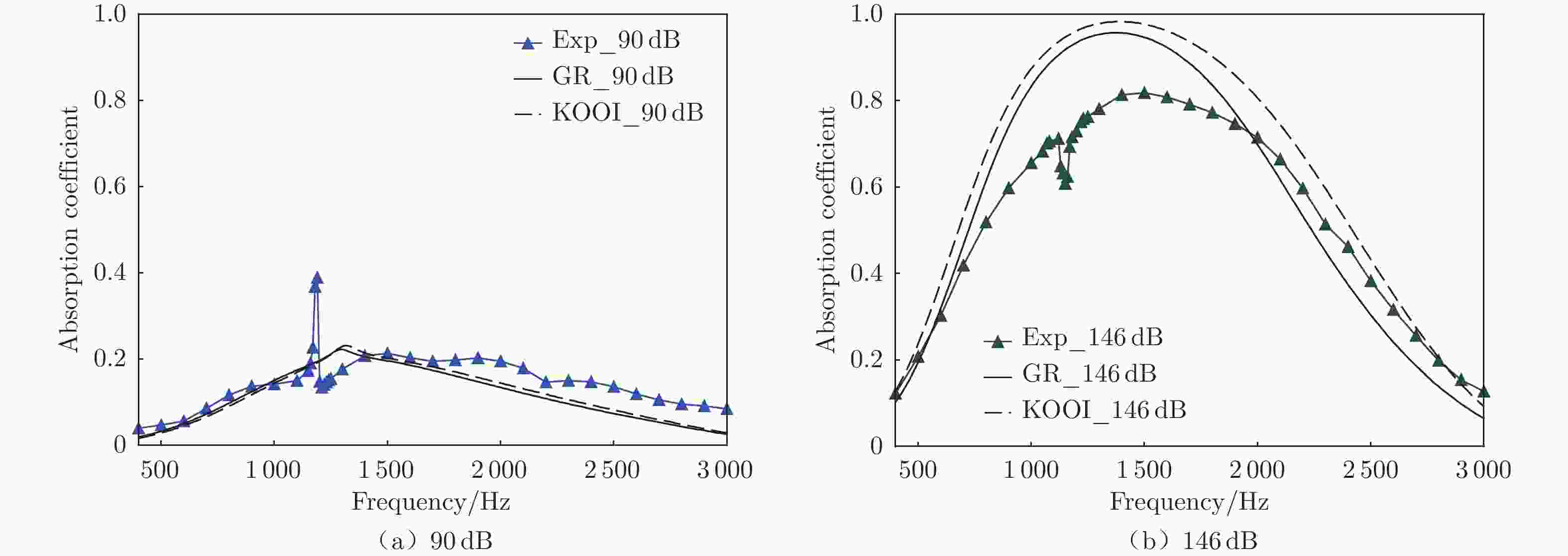
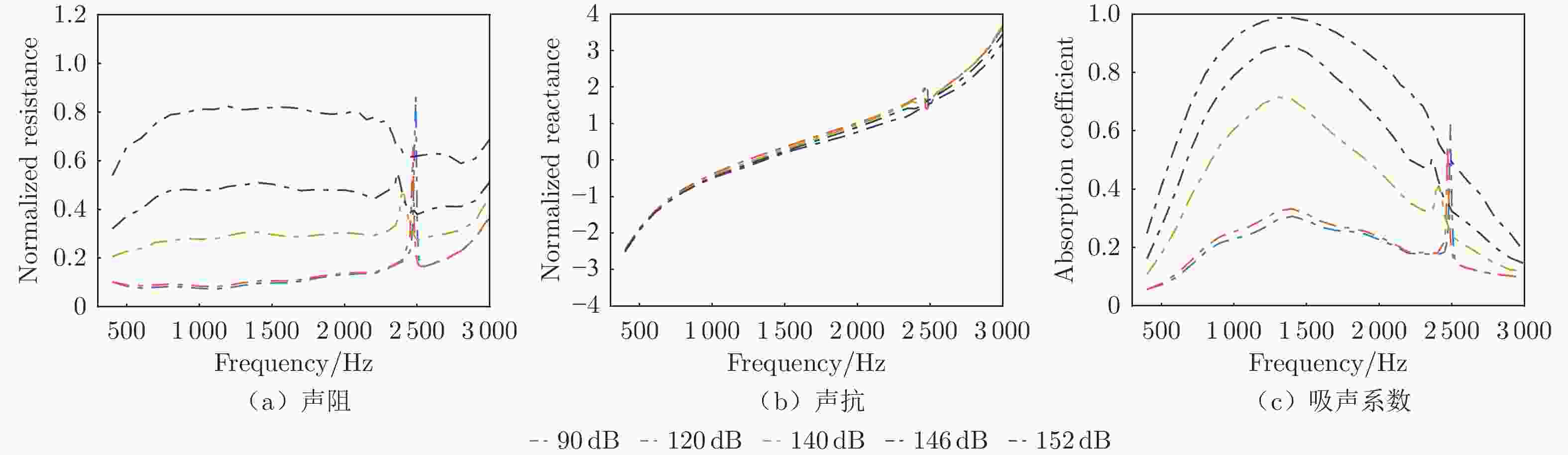
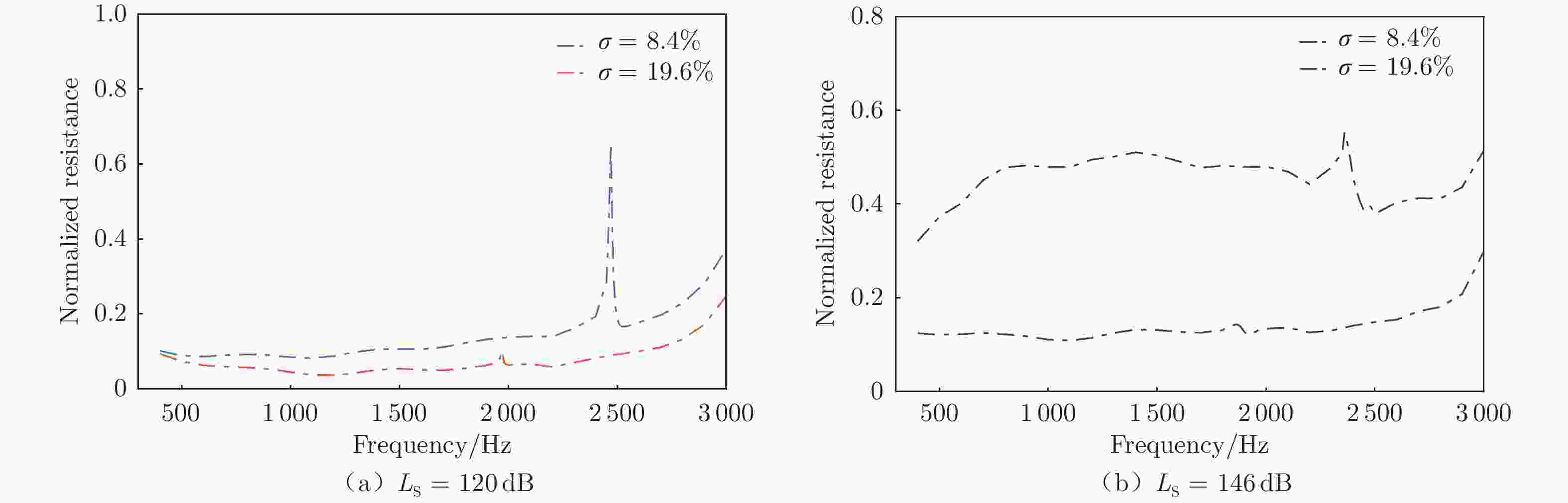
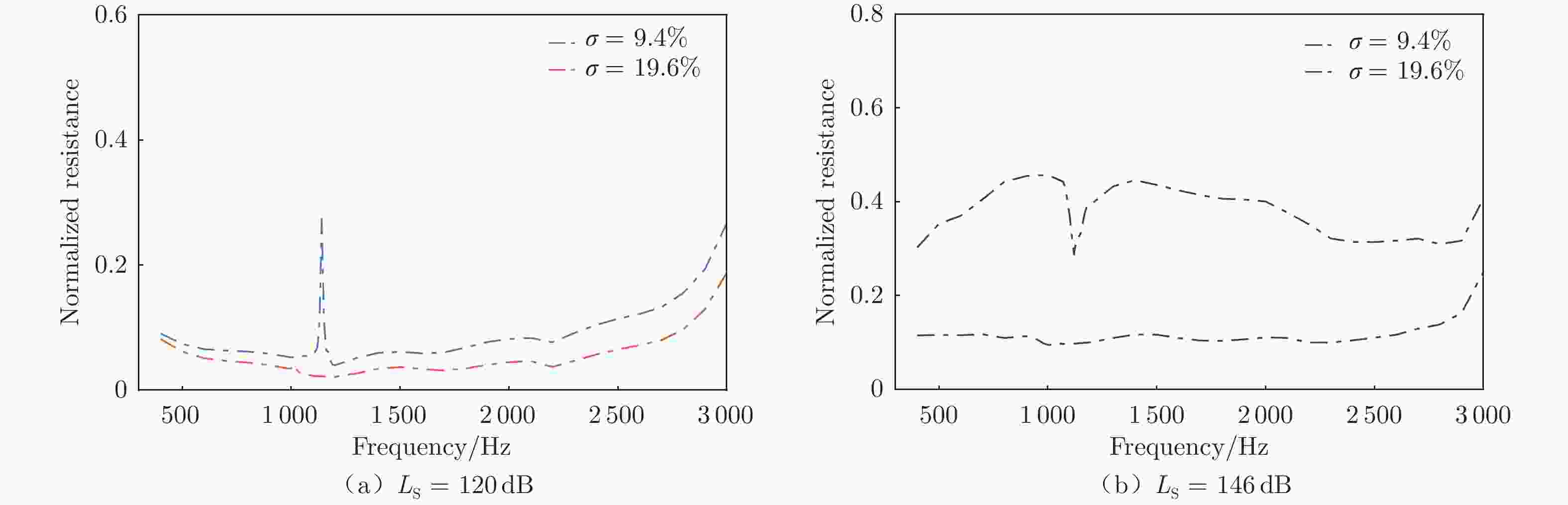
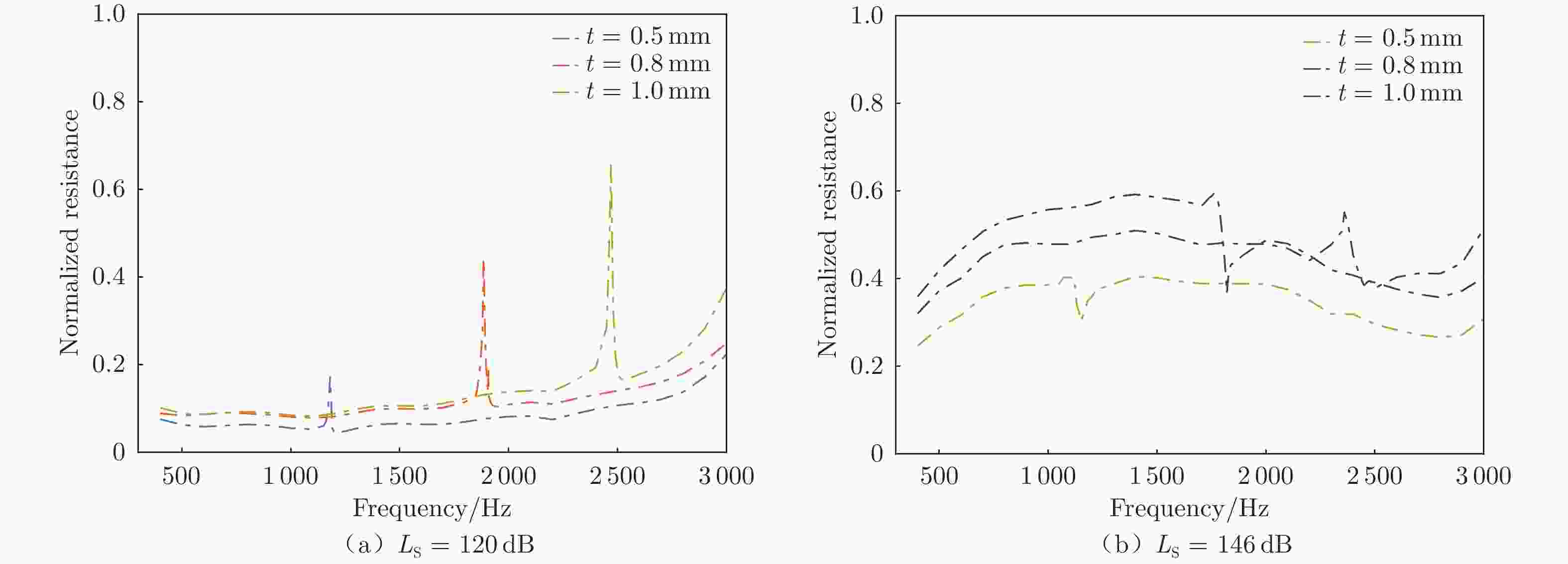
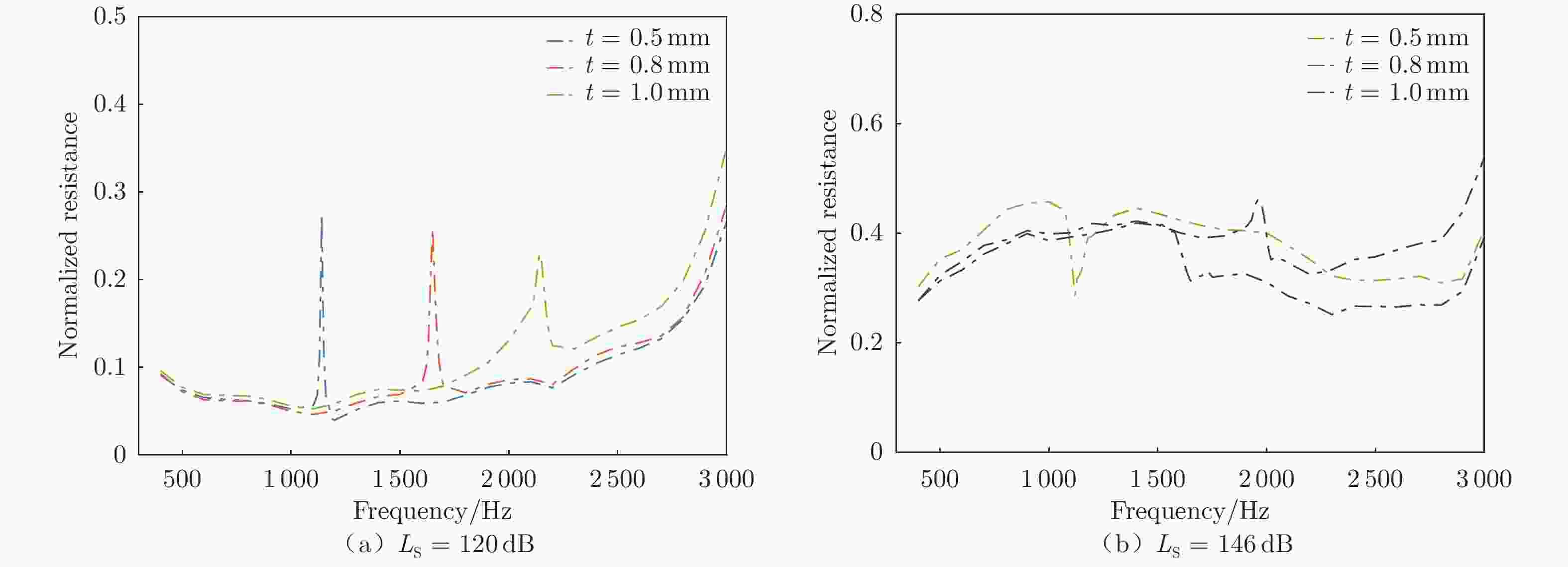
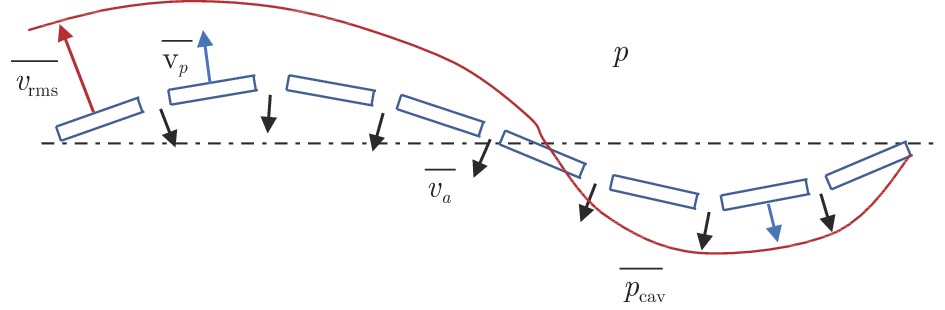
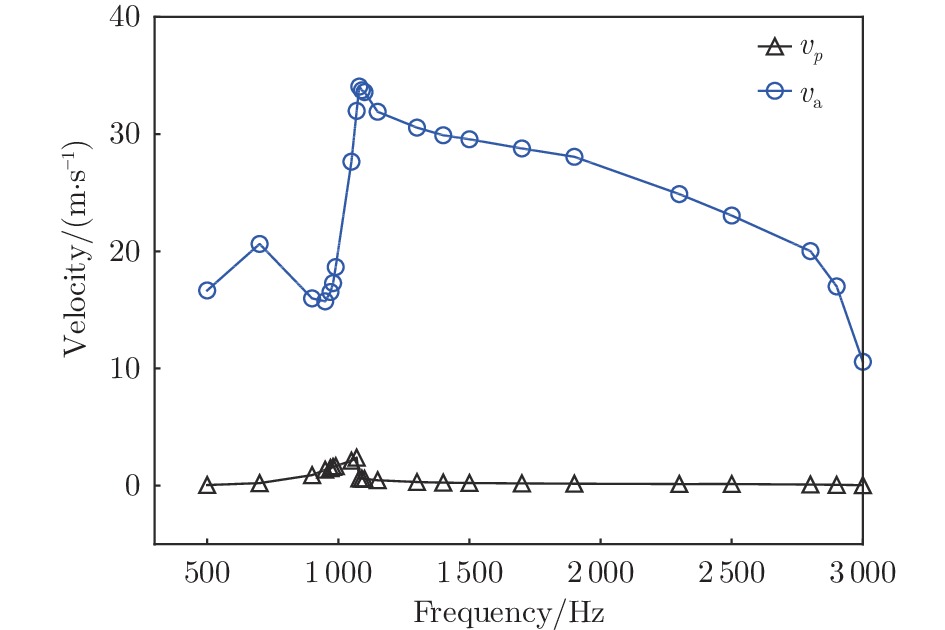
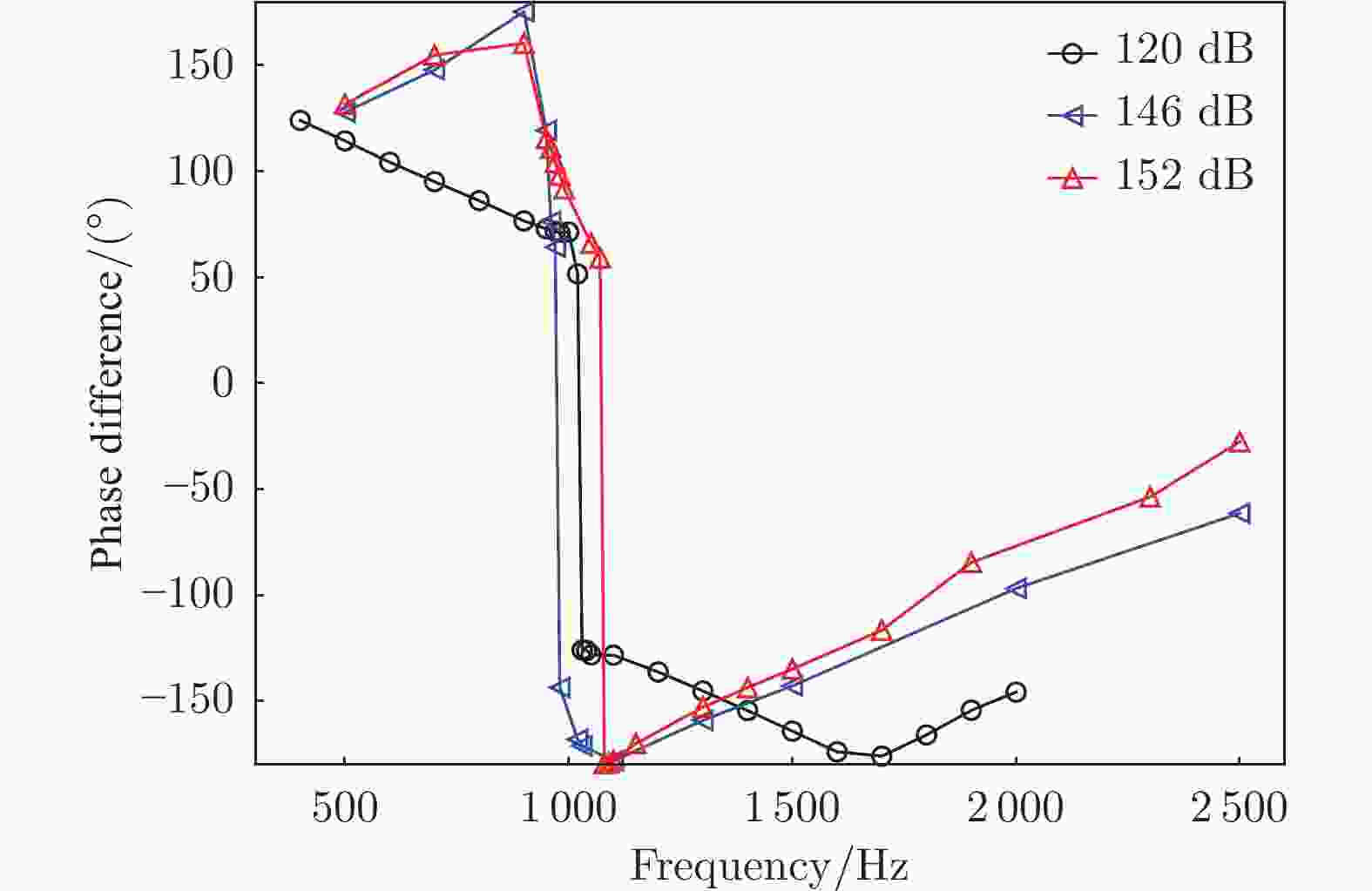
摘要: 声衬在高声压级声波激发下产生声振响应,刚性假设不再成立,其结构振动会对吸声产生一定影响。本文针对振动对声衬吸声的影响和声振响应开展实验研究,通过参数化研究,获得了不同工况和不同穿孔板几何参数下声振响应对声阻抗的影响规律。实验结果表明:穿孔板振动会导致声阻在结构共振频率处出现波峰或波谷,吸声系数出现“额外”的吸声波峰或吸声波谷;穿孔率和声压级的增大会减弱振动的影响,且存在一个临界穿孔率;穿孔板参数会影响高声压级下结构振动导致声阻变化的特征;在结构共振频率附近,小孔–面板速度相位差会发生突变,导致相对速度增大,吸声效果改变。Abstract: The acoustic liners produce vibroacoustic response under the excitation of sound waves at high sound pressure level, and the rigid structure assumption is no longer applied. Their structural vibrations have a certain impact on sound absorption performance. The work presented here is an experimental study on the influence of panel vibrations on sound absorption and vibroacoustic response, and the influence law of vibroacoustic response on acoustic impedance under different perforated plate geometric parameters is obtained through parametric research. The experimental results show that the vibration of the perforated plate causes resistance to the generation of peaks or dips at the structural resonance frequency, and the sound absorption coefficient generates extra absorption peaks or dips that cannot be understood assuming rigid acoustic liners. The increase of the perforation rate and sound pressure level suppresses the influence of vibration, and there is a critical perforation rate. Perforated plate parameters affect the characteristics of resistance changes caused by structural vibration at high sound pressure levels. The phase difference between the small holes and the panel near the structure resonance frequency changes abruptly, resulting in an increase in the relative velocity and a change in the sound absorption performance.
-
Key words:
- acoustic liner /
- acoustic impedance /
- vibroacoustic
-
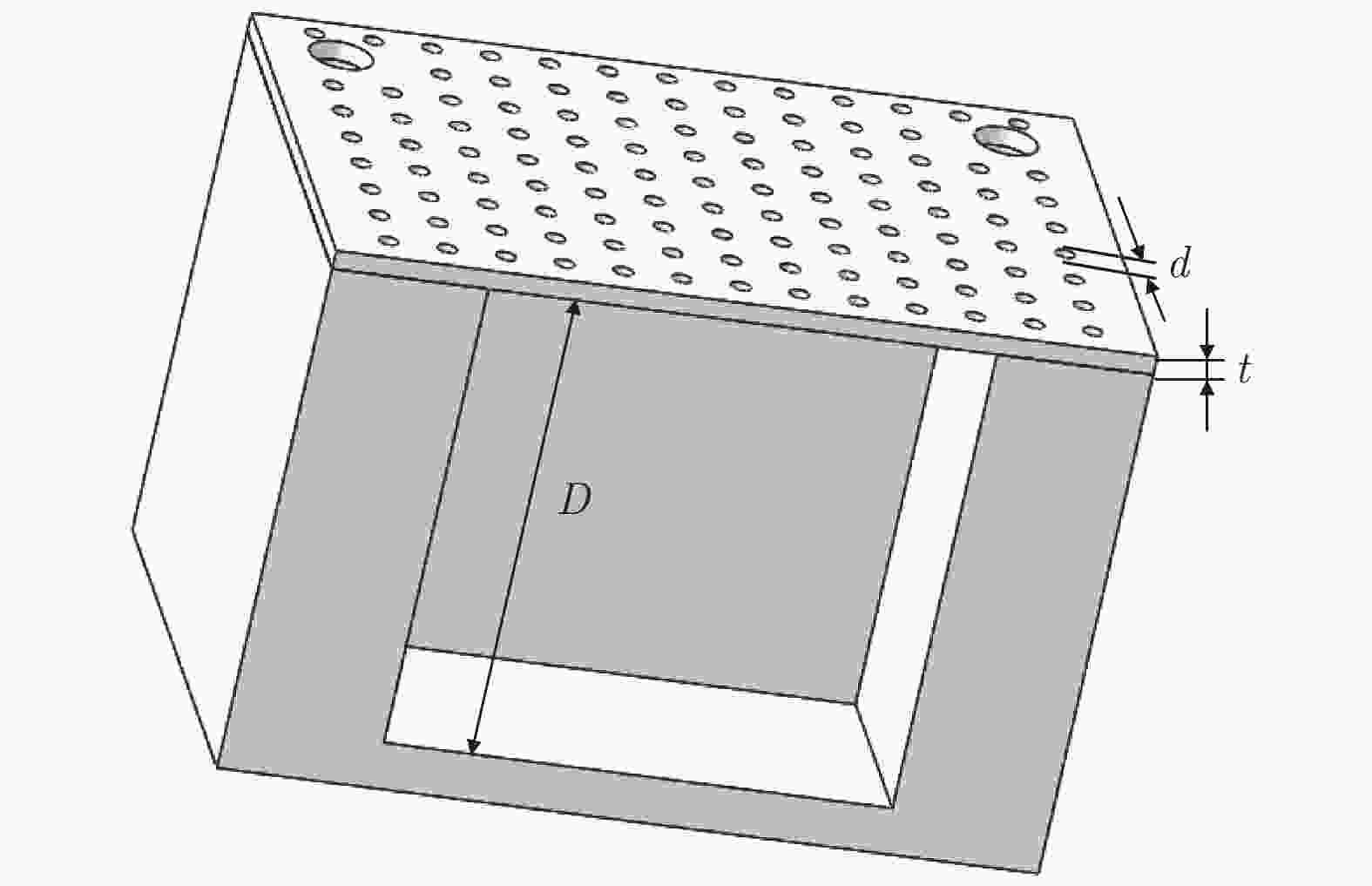
表 1 声衬结构参数
Table 1. Summary of liner structure parameters
声衬编号 孔径d/mm 穿孔率σ/% 板厚t/mm 腔深D/mm L1 1 8.4 0.5 50 L2 1 8.4 0.8 50 L3 1 8.4 1.0 50 L4 1 19.6 1.0 50 L5 2 9.4 0.5 50 L6 2 9.4 0.8 50 L7 2 9.4 1.0 50 L8 2 19.6 0.5 50 L9 2 19.6 0.8 50 L10 2 19.6 1.0 50 -
[1] NAYFEH A H, KAISER J E, TELIONIS D P. Acoustics of aircraft engine-duct systems[J]. AIAA Journal, 1975, 13(2): 130–153. doi: 10.2514/3.49654 [2] CUMPSTY N A. Review—A critical review of turbomachinery noise[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 1977, 99(2): 278–293. doi: 10.1115/1.3448745 [3] MAA D Y. Potential of microperforated panel absorber[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1998, 104(5): 2861–2866. doi: 10.1121/1.423870 [4] SIVIAN L J. Acoustic impedance of small orifices[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1935, 7(2): 94–101. doi: 10.1121/1.1915795 [5] INGARD U, LABATE S. Acoustic circulation effects and the nonlinear impedance of orifices[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1950, 22(2): 211–218. doi: 10.1121/1.1906591 [6] INGARD U, ISING H. Acoustic nonlinearity of an orifice[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1967, 42(1): 6–17. doi: 10.1121/1.1910576 [7] MELLING T H. The acoustic impendance of perforates at medium and high sound pressure levels[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1973, 29(1): 1–65. doi: 10.1016/S0022-460X(73)80125-7 [8] GUESS A W. Calculation of perforated plate liner parameters from specified acoustic resistance and reactance[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1975, 40(1): 119–137. doi: 10.1016/S0022-460X(75)80234-3 [9] YU J, RUIZ M, KWAN H W. Validation of Goodrich perforate liner impedance model using NASA langley test data[C]//Proc of the 14th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference (29th AIAA Aeroacoustics Conference). 2008. doi: 10.2514/6.2008-2930 [10] KOOI J W, SARIN S L, FOKKER B V. An experimental study of the acoustic impedance of Helmholtz resonator arrays under a turbulent boundary layer[C]//Proc of the 7th AIAA Aeroacoustics Conference. 1981. doi: 10.2514/6.1981-1998 [11] CUMMINGS A. The effects of grazing turbulent pipe-flow on the impedance of an orifice[J]. Acta Acustica United With Acustica, 1986, 61(4): 233–242. [12] NARK D M, JONES M G, SUTLIFF D L. Modeling of broadband liners applied to the advanced noise control fan[C]//Proc of the 21st AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference. 2015. doi: 10.2514/6.2015-2693 [13] NARK D M, JONES M G, SUTLIFF D L. Further development and assessment of a broadband liner optimization process[C]//Proc of the 22nd AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference. 2016. doi: 10.2514/6.2016-2784 [14] SYED A A, ICHIHASHI F. The modeling and experimental validation of the acoustic impedance of multi-degrees-of-freedom liners[C]//Proc of the 14th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference (29th AIAA Aeroacoustics Conference). 2008. doi: 10.2514/6.2008-2927 [15] JONES M G, HOWERTON B M, AYLE E. Evaluation of parallel-element, variable-impedance, broadband acoustic liner concepts[C]//Proc of the 18th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference (33rd AIAA Aeroacoustics Conference). 2012. doi: 10.2514/6.2012-2194 [16] JONES M G, WATSON W R, NARK D M, et al. Evaluation of a variable-impedance ceramic matrix composite acoustic liner[C]//Proc of the 20th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference. 2014. doi: 10.2514/6.2014-3352 [17] JONES M G, WATSON W R, NARK D M, et al. Optimization of variable-depth liner configurations for increased broadband noise reduction[C]//Proc of the 22nd AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference. 2016. doi: 10.2514/6.2016-2783 [18] BECK B S, SCHILLER N H, JONES M G. Impedance assessment of a dual-resonance acoustic liner[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2015, 93(4): 15–22. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2015.01.011 [19] MEI J, MA G C, YANG M, et al. Dark acoustic metamaterials as super absorbers for low-frequency sound[J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3: 756. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1758 [20] LEE J, SWENSON G W. Compact sound absorbers for low frequencies[J]. Noise Control Engineering Journal, 1992, 38(3): 109–117. doi: 10.3397/1.2827811 [21] TOYODA M, MU R L, TAKAHASHI D. Relationship between Helmholtz-resonance absorption and panel-type absorption in finite flexible microperforated-panel absorbers[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2010, 71(4): 315–320. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2009.10.007 [22] SAKAGAMI K, MORIMOTO M, YAIRI M. A note on the effect of vibration of a microperforated panel on its sound absorption characteristics[J]. Acoustical Science and Technology, 2005, 26(2): 204–207. doi: 10.1250/ast.26.204 [23] LEE Y Y, LEE E W M, NG C F. Sound absorption of a finite flexible micro-perforated panel backed by an air cavity[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2005, 287: 227–243. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2004.11.024 [24] TAKAHASHI D, TANAKA M. Flexural vibration of perforated plates and porous elastic materials under acoustic loading[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2002, 112(4): 1456–1464. doi: 10.1121/1.1497624 [25] TOYODA M, TAKAHASHI D. Sound transmission through a microperforated-panel structure with subdivided air cavities[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2008, 124(6): 3594–3603. doi: 10.1121/1.3001711 [26] BRAVO T, MAURY C, PINHÈDE C. Enhancing sound absorption and transmission through flexible multi-layer micro-perforated structures[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2013, 134(5): 3663–3673. doi: 10.1121/1.4821215 [27] BRAVO T, MAURY C, PINHÈDE C. Sound absorption and transmission through flexible micro-perforated panels backed by an air layer and a thin plate[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2012, 131(5): 3853–3863. doi: 10.1121/1.3701987 [28] CHUNG J Y, BLASER D A. Transfer function method of measuring in-duct acoustic properties. I. Theory[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1980, 68(3): 907–913. doi: 10.1121/1.384778 [29] CHUNG J Y, BLASER D A. Transfer function method of measuring in-duct acoustic properties. II. Experiment[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1980, 68(3): 914–921. doi: 10.1121/1.384779 -








 下载:
下载: