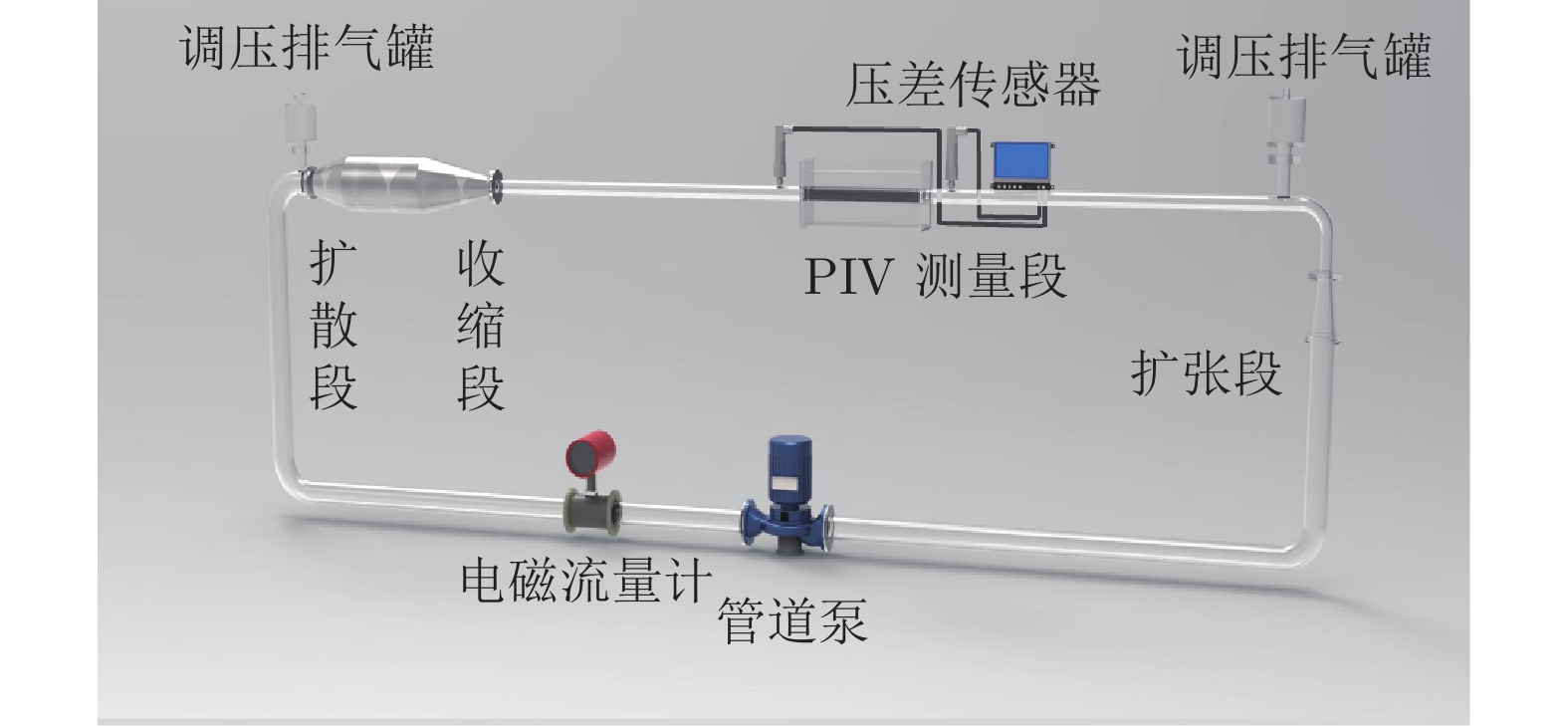
Experimental study of the characteristics of very-large-scale motions in polymer pipe flows
-
摘要: 高聚物减阻在管道输送中发挥着重要作用。管道湍流中的相干结构与高聚物减阻机理密切相关。实际工程中的管道流动大多为高雷诺数流动,高雷诺数管道流中最主要的含能相干结构为10倍管径量级的超大尺度结构。本文对高雷诺数高聚物管道流中的超大尺度结构进行实验研究。开展了4种高聚物浓度(以质量分数表征)、3种雷诺数共12组TR-PIV(Time-Resolved Particle Image Velocimetry)实验,使用预乘谱对超大尺度结构的尺度和强度特征进行了分析。研究结果表明,在相同雷诺数下,随着高聚物浓度增大,中心流区超大尺度结构的尺度和强度均明显增大,且与大尺度结构的强度之比也显著增大。在较高浓度下,超大尺度结构取代大尺度结构,成为了外区的主导含能结构。Abstract: Polymer drag reduction plays an important role in pipeline transportation. The drag reduction mechanism of polymer solutions is directly related to the coherent structure in pipe flows. High Reynolds number flows are the mainstream in the actual engineering, and very-large-scale structures with the streamwise length scale of 10 times pipe diameter are the most significant coherent structures in high Reynolds number pipe flows. In the present paper, experimental study is carried out on the very-large-scale structures in high Reynolds number polymer pipe flows. Premultiplied spectral analysis is used to examine the scale and strength properties of the very-large-scale structures in 12 sets of TR-PIV experiments with 4 polymer concentrations and 3 Reynolds numbers. The findings demonstrate that the scale and intensity of the very-large-scale structures in the central flow region significantly increase with an increase in the polymer concentration under the same Reynolds number, and the ratio of the intensity of the very-large-scale structures to that of the large-scale structures also significantly increases. The large-scale structure is replaced by the very-large-scale structure, which thereafter dominates as the main energy-containing structures in the outer region at elevated concentrations.
-
表 1 各测次实验参数
Table 1. Experimental parameters for each measurement
测次 c/
10−6μ/
(10−3pa·s)∆p/
kPaRe u* $\overline u $/
(m·s−1)Reτ Q1 0 0.89 3.25 57752 0.11 2.57 2562 Q2 0 0.89 6.25 83595 0.16 3.72 3553 Q3 0 0.89 10.60 112134 0.21 4.99 4627 P11 30 0.93 3.40 57634 0.12 2.68 2507 P12 30 0.93 6.60 84323 0.16 3.92 3494 P13 30 0.93 10.88 110430 0.21 5.14 4486 P21 60 0.97 3.68 59835 0.12 2.91 2501 P22 60 0.97 7.05 85773 0.17 4.16 3462 P23 60 0.97 11.92 116144 0.22 5.63 4502 P31 100 1.04 4.28 60288 0.13 3.14 2516 P32 100 1.04 8.32 89231 0.18 4.64 3508 P33 100 1.04 13.74 118462 0.23 6.16 4508 -
[1] 张兵强, 梁光川, 郦利民, 等. 高分子聚合物的湍流减阻机理[J]. 油气储运, 2012, 31(12): 895–897. doi: 10.6047/j.issn.1000-8241.2012.12.005ZHANG B Q, LIANG G C, LI L M, et al. Mechanism of turbulent drag reduction of polymer[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2012, 31(12): 895–897. doi: 10.6047/j.issn.1000-8241.2012.12.005 [2] TOMS B A. Some observations on the flow of linear polymer solutions through straight tubes at large Reynolds numbers[C]//Proc of the 1st International Congress on Rheology, Volume 2. 1948: 135-141. [3] 左艳梅. 超高分子量聚长链α-烯烃的合成及应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2006.ZUO Y M. Synthesis and application of the poly (long chain α-olefins) with ultra high molecular weight[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2006. [4] KLINE S J, REYNOLDS W C, SCHRAUB F A, et al. The structure of turbulent boundary layers[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1967, 30(4): 741–773. doi: 10.1017/s0022112067001740 [5] 郑晓静, 王国华. 高雷诺数壁湍流的研究进展及挑战[J]. 力学进展, 2020, 50: 202001. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-19-009ZHENG X J, WANG G H. Progresses and challenges of high Reynolds number wall-bounded turbulence[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2020, 50: 202001. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-19-009 [6] ADRIAN R J. Hairpin vortex organization in wall turbulence[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2007, 19(4): 457. doi: 10.1063/1.2717527 [7] ADRIAN R J, MEINHART C D, TOMKINS C D. Vortex organization in the outer region of the turbulent boundary layer[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2000, 422(1): 1–54. doi: 10.1017/S0022112000001580 [8] DUAN Y C, ZHONG Q, WANG G Q, et al. Additional spanwise vortices near the free surface in open channel flows[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 924: R3. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2021.641 [9] ZHONG Q, LI D X, CHEN Q G, et al. Coherent structures and their interactions in smooth open channel flows[J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 2015, 15(3): 653–672. doi: 10.1007/s10652-014-9390-z [10] ADRIAN R J, MARUSIC I. Coherent structures in flow over hydraulic engineering surfaces[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 2012, 50(5): 451–464. doi: 10.1080/00221686.2012.729540 [11] DUAN Y C, ZHONG Q, WANG G Q, et al. Contributions of different scales of turbulent motions to the mean wall-shear stress in open channel flows at low-to-moderate Reynolds numbers[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 918: A40. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2021.236 [12] DUAN Y C, CHEN Q G, LI D X, et al. Contributions of very large-scale motions to turbulence statistics in open channel flows[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2020, 892: A3. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2020.174 [13] ZHONG Q, CHEN Q G, WANG H, et al. Statistical analysis of turbulent super-streamwise vortices based on observations of streaky structures near the free surface in the smooth open channel flow[J]. Water Resources Research, 2016, 52(5): 3563–3578. doi: 10.1002/2015wr017728 [14] HUTCHINS N, MARUSIC I. Large-scale influences in near-wall turbulence[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2007, 365(1852): 647-664. DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2006.1942. [15] MARUSIC I, MATHIS R, HUTCHINS N. Predictive model for wall-bounded turbulent flow[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5988): 193–196. doi: 10.1126/science.1188765 [16] McCOMB W D, RABIE L H. Local drag reduction due to injection of polymer solutions into turbulent flow in a pipe. Part I: Dependence on local polymer concentration[J]. AIChE Journal, 1982, 28(4): 547–557. doi: 10.1002/aic.690280405 [17] MCCOMB W D, RABIE L H. Local drag reduction due to injection of polymer solutions into turbulent flow in a pipe. Part II: laser-doppler measurements of turbulent structure[J]. AIChE Journal, 1982, 28(4): 558–565. doi: 10.1002/aic.690280406 [18] 王超伟, 杨绍琼, 姜楠. 高分子溶液对湍流边界层减阻机理的实验研究[J]. 应用力学学报, 2021, 38(6): 2384–2391. doi: 10.11776/cjam.38.06.A127WANG C W, YANG S Q, JIANG N. Experimental investigation of drag reduction in turbulent boundary layer with polymer additives solution[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2021, 38(6): 2384–2391. doi: 10.11776/cjam.38.06.A127 [19] GUAN X L, YAO S Y, JIANG N. A study on coherent structures and drag-reduction in the wall turbulence with polymer additives by TRPIV[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2013, 29(4): 485–493. doi: 10.1007/s10409-013-0035-0 [20] KIM K, LI C F, SURESHKUMAR R, et al. Effects of polymer stresses on eddy structures in drag-reduced turbulent channel flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2007, 584: 281–299. doi: 10.1017/s0022112007006611 [21] DUBIEF Y, TERRAPON V E, WHITE C M, et al. New answers on the interaction between polymers and vortices in turbulent flows[J]. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion, 2005, 74(4): 311–329. doi: 10.1007/s10494-005-9002-6 [22] DE ANGELIS E, CASCIOLA C M, PIVA R. DNS of wall turbulence: dilute polymers and self-sustaining mechanisms[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2002, 31(4-7): 495–507. doi: 10.1016/s0045-7930(01)00069-x [23] SIBILLA S, BARON A. Polymer stress statistics in the near-wall turbulent flow of a drag-reducing solution[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2002, 14(3): 1123–1136. doi: 10.1063/1.1448497 [24] KIM K, ADRIAN R J, BALACHANDAR S, et al. Dynamics of hairpin vortices and polymer-induced turbulent drag reduction[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100(13): 134504. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.134504 [25] ZHU L, XI L. Vortex dynamics in low- and high-extent polymer drag reduction regimes revealed by vortex tracking and conformation analysis[]. Physics of Fluids, 2019, 31(9): 095103. doi: 10.1063/1.5118251. [26] ZHANG Y B, BODENSCHATZ E, XU H T, et al. Experimental observation of the elastic range scaling in turbulent flow with polymer additives[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(14): eabd3525. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abd3525 [27] 盖春燕. 高泥化煤泥水特性与处理工艺研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2006.GAI C Y. The characteristics and processing technology study of high marlaceous slurry[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2006. -








 下载:
下载: